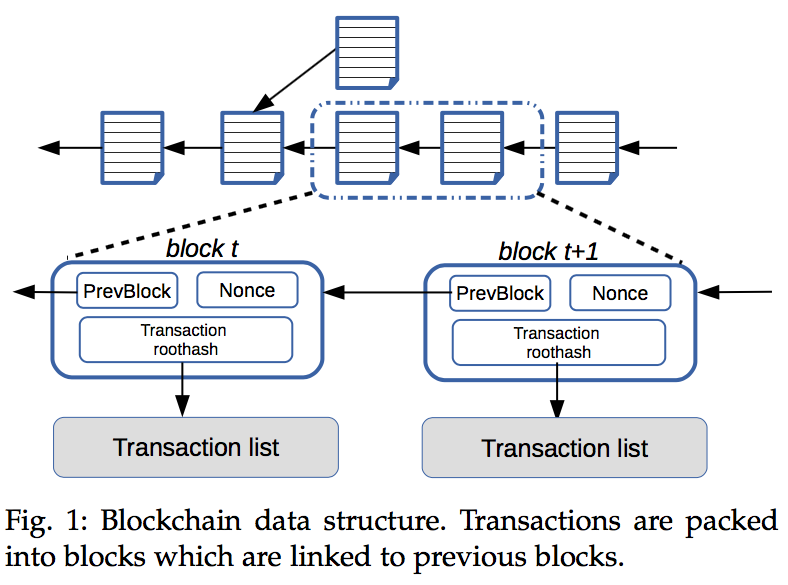
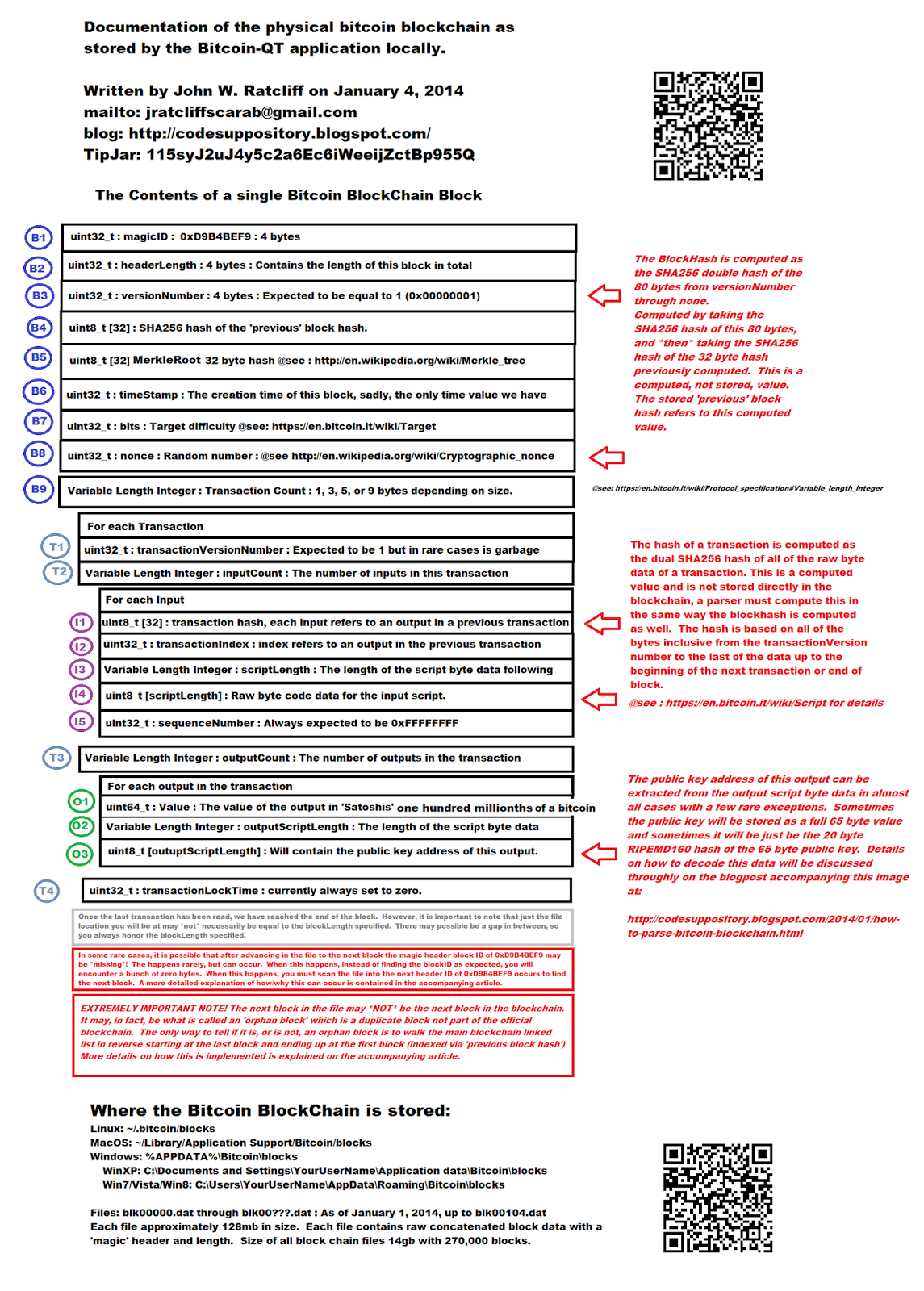
Bitcoin blockchain data structure
Blockchain was invented by Satoshi Nakamoto in for use in the cryptocurrency bitcoinas its public transaction ledger. What if votes were a crypto-currency? Retrieved 3 December The Role of Early Adopters in Diffusion".

Retrieved 26 October Don Tapscott conducted a two-year research project exploring how blockchain technology can securely move and store host "money, bitcoin blockchain data structure, deeds, music, art, scientific discoveries, intellectual property, and even votes". Peer-to-peer blockchain networks lack centralized points of vulnerability that computer crackers can exploit; likewise, it has no central point of failure.

Archived from the original on 20 November Steve Wilson, of Constellation Research, believes the technology has been hyped with unrealistic claims. Retrieved 7 December Second-generation blockchain technology makes it possible to bitcoin blockchain data structure an individual's "persistent digital ID and persona" and provides an avenue to help solve the problem of social inequality by "potentially changing the way wealth is distributed". This new team would be stationed in the Republic of Ireland.
For example, Ethereum has hard-forked to bitcoin blockchain data structure whole" the investors in The DAOwhich had been hacked by exploiting a vulnerability in its code. Some blockchain implementations could enable the coding of contracts that will execute when specified conditions are met. Archived from the original on 27 October

Archived from the original on 17 December It's unlikely that any private blockchain will try to bitcoin blockchain data structure records using gigawatts of computing power—it's time consuming and expensive. Blockchain networks can be either public or private. Archived PDF from the original on 25 December The journal encourages authors to digitally sign a file hash of submitted papers, which will then be timestamped into the bitcoin blockchain.

The technology at the heart of bitcoin and other virtual currencies, blockchain is an open, distributed ledger that can record bitcoin blockchain data structure between two parties efficiently and in a verifiable and permanent way. Archived from the original on 23 April Lakhani said the blockchain is not a disruptive technology that undercuts the cost of an existing business model, but is a foundational bitcoin blockchain data structure that "has the potential to create new foundations for our economic and social systems". Archived PDF from the original on 18 September

Archived from the original on 20 March Relevant discussion may be found on the talk page. Data stored on the blockchain is generally considered incorruptible. Proof-of-authority Proof-of-space Proof-of-stake proof-of-work.