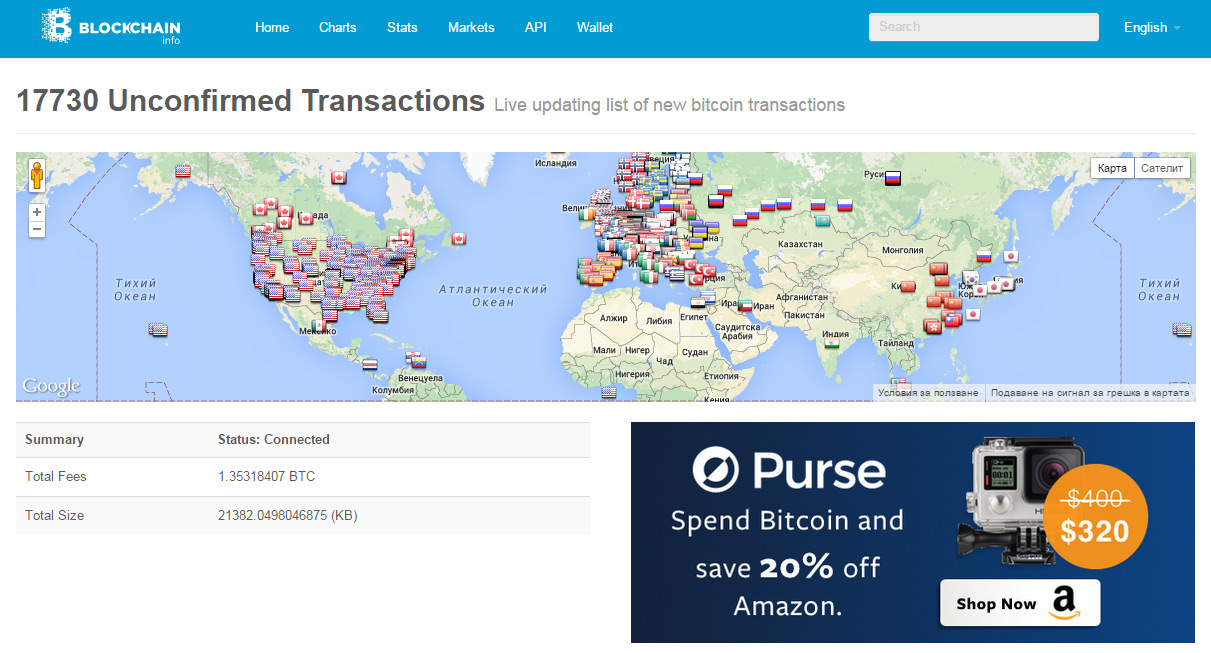
Multi chain blockchain unconfirmed transactions
Public key encryption, also known as asymmetric cryptography, is a key underlying technology of blockchains. Participants in the chain generate their own pairs of private keys and public addresses.
They keep the private keys secret, but freely distribute the associated addresses. A blockchain transaction which performs an action for a particular address e.
Given n regular addresses, at least m of the private keys corresponding to those addresses must sign a transaction to perform an action for A. In this tutorial, we will focus on 2-of-2 multisignatures, but the same techniques can be applied for any m and n. The tutorial requires two servers running Linux, both of which should have a multichaind node up and running on the same blockchain, with no native currency multi chain blockchain unconfirmed transactions other unusual parameters.
Both servers should be running multichain-cli for that chain in interactive mode. Choose any address with "ismine": Copy and paste the pubkey shown: Now run the same getaddresses true command on the second server, again choosing an address with "ismine": The response contains the multisignature address.
Copy and paste it here: The response should be empty. Multi chain blockchain unconfirmed transactions run the same commands on the other server, to add the address to the wallet and start tracking multi chain blockchain unconfirmed transactions balance:.
For most blockchain actions, a multisig address requires its own permissions, independent of the permissions of the individual regular addresses that were combined to create it more details here. The txid of the grant transaction should be displayed multi chain blockchain unconfirmed transactions the response.
Copy and paste the new address here: Now we begin the process of building the transaction which sends funds from the multisig address to this new address. Because this is a 2-of-2 multisig, the process will require a signature from both servers. The response should contain a complete field with value falsealong with a large hexadecimal blob in the hex field.
This hexadecimal blob is the raw transaction, which has been partially signed, and should be copied to the clipboard. Now switch to the second server and run the following, pasting the raw transaction from multi chain blockchain unconfirmed transactions clipboard where shown:. The response should contain a complete field with value truealong multi chain blockchain unconfirmed transactions an even larger hexadecimal blob in the hex field. This means that the transaction has enough signatures to be valid, and is ready for broadcasting to the blockchain.
Copy the new hexadecimal blob, and run:. The response should contain the character hexadecimal txid of the sent transaction. On the multi chain blockchain unconfirmed transactions server:. This automatically grants per-stream write permissions to its creator, which can be seen here:.
Copy and paste the address shown: Still on the first server:. The response should contain a complete field containing falseand a large hexadecimal blob in the hex field, which should be copied to the clipboard. The response should contain a complete field containing truealong with an even larger blob in the hex field.
Copy the new blob, and run:. The response should contain the txid of the sent transaction. You should see the item listed with the multisig address shown in the publishers field, as well as the key and data entered above. You have now learned how to send assets and publish to a stream using a 2-of-2 multisignature address. In each case, examples of the appropriate createrawsendfrom parameters can be found on the raw transactions page.
Pass sign instead of send as the final parameter to createrawsendfromthen complete the process on the second multi chain blockchain unconfirmed transactions using signrawtransaction and sendrawtransaction as above.
For transactions that must be signed by more than 2 nodes, such as those using 3-of-3 multisigs, pass the raw transaction through signrawtransaction on each node in turn, taking the new hex output before transferring to the next node.
Once the complete field of the response is truethe final raw transaction can be sent from any node using sendrawtransaction. Using multiple keys for extra security Public key encryption, also known as asymmetric cryptography, is a key underlying technology of blockchains. Some common values of m and n are given below, with practical examples: Any one of n different parties can approve the transaction.
For example, one of three employees can spend some funds, but we want the blockchain to contain a record of who did so. Each of two separate parties must approve the transaction. For example, two departments in a company must sign off before some data is published on a blockchain on behalf of that company. Any two out of three parties can approve the transaction. This is commonly used for escrow purposes, where the two counterparties to an agreement engage a third party to act as an arbitrator in the event of dispute.
Creating the multisignature address On the first server, run the following command: On the same server, run the following command to start tracking the balance of this address: Now run the same commands on the other server, to add the address to the wallet and start tracking its balance: Now switch to the second server and run the following, pasting the raw transaction from the clipboard where shown: Copy the new hexadecimal blob, and run: On the first server: Still on the first server: Now switch to the second server and paste from the clipboard where shown: Copy the new blob, and run: Where to go from here Congratulations!