8 bit ripple carry adder critical path definition

The layout of a ripple-carry adder is simple, which allows fast design time; however, the ripple-carry adder is relatively slow, since each full adder must wait for the carry bit to be calculated from the previous full adder. Other adder designs include the carry-select adderconditional sum addercarry-skip adderand carry-complete adder. These block based adders include the carry-skip or carry-bypass adder which will determine P and 8 bit ripple carry adder critical path definition values for each block rather than each bit, and the carry select adder which pre-generates the sum and carry values for either possible carry input 0 or 1 to the block, using multiplexers to select the appropriate result when the carry bit is known. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia.
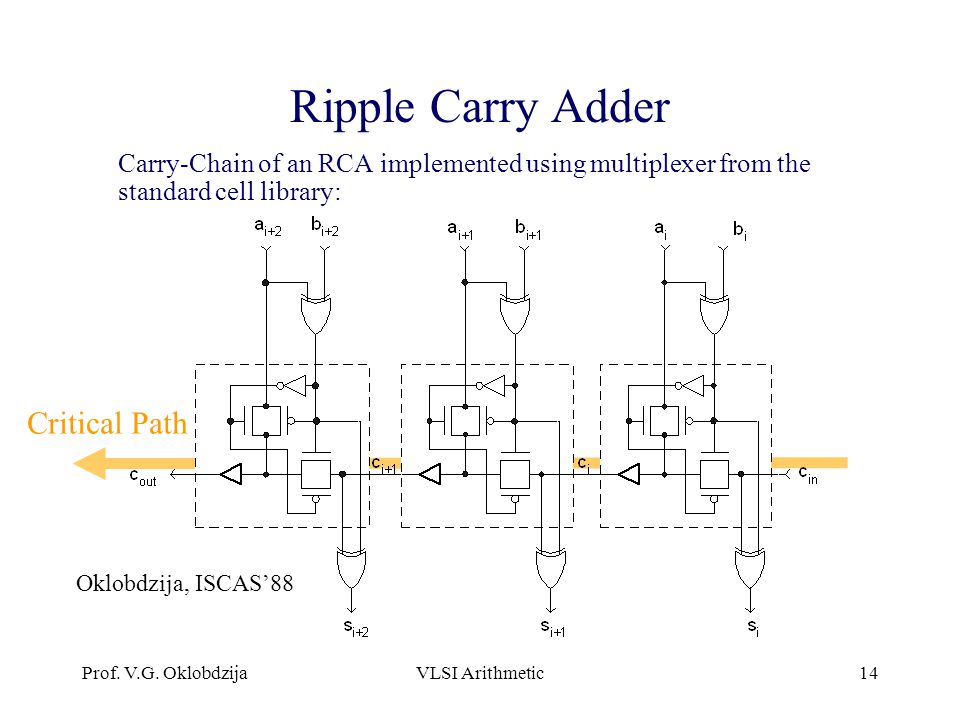
Views Read Edit View history. Some other multi-bit adder architectures break the adder into blocks. Assumed that an XOR-gate takes 1 delays to complete, the delay imposed by the critical path of a full adder is equal to.

It has two outputs, sum S and carry C. The sum and the carry may be fed into two inputs of the subsequent 3-number adder without having to wait for propagation of a carry signal. Instead, three-input adders are used, generating two results: