Blockchain uk not working
Blockchain and distributed ledger technology offers significant and scalable processing power, high accuracy rates, and apparently unbreakable security at a significantly reduced cost compared to the traditional systems the technology could replace, such as settlement, trading or accounting systems. Like all new technology however, it poses challenges for suppliers and customers.
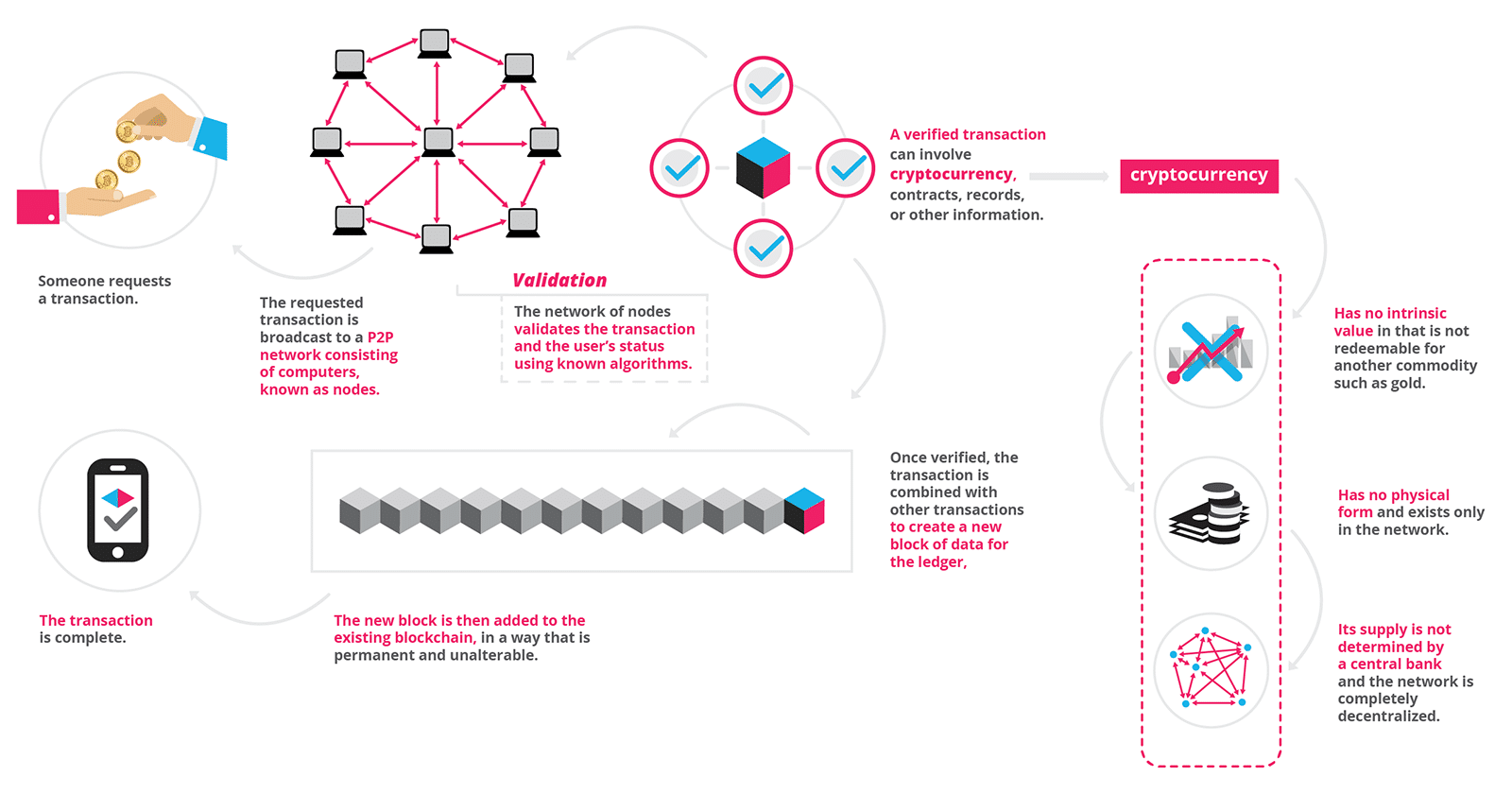
So what are the key issues in relation to blockchain and distributed ledger technology? In its simplest form, blockchain is a decentralised technology or distributed ledger on which transactions are anonymously recorded. The ledger contains a continuous and complete record the chain of all transactions performed which are grouped blockchain uk not working blocks: A transaction can only be verified and form part of a candidate block if all the nodes on the network confirm that the transaction is valid.
A block generally contains four pieces of information: Once information is entered on the blockchain, it is extremely difficult to alter: Assets and information about transactions can be stored and tracked without the involvement of a typical intermediary, such as a bank, or a central authority or some other trusted third party. A blockchain network may be public and open permissionless like the internet or structured within a private group like an intranet permissioned.
These blockchains use a variety of means to ensure the identity of parties to a transaction and to achieve consensus as to the validity of transactions.
Only specific authorised participants are given access and are known within the network. One of the key attributes of blockchain is that it is said to be virtually unhackable due to the complex cryptography and the distributed nature of the ledger: This is in stark contrast to the weakness of so many existing highly centralised systems with a single point of failure. As a consequence, in order to avoid defeating the very purpose and attraction of the blockchain, customers may need to resist the temptation to require bespoke developments and modifications or at least understand the potential consequences of doing sowhilst vendors will be required to blockchain uk not working both the solution, and any necessary back-up protocols, to avoid introducing security vulnerabilities in the first place and to provide safeguards in the event this is not completely successful.
Blockchain databases grow rapidly in size as new transactions are written, and there is a concern that the size of database required, and the consequent speed of access, may make it unsuitable for certain forms of transactions blockchain uk not working speed is of the essence.
At the moment, many blockchain solutions are in a development or low adoption phase and, as a consequence, the technology and policies offered are relatively untrusted. Many organisations will therefore be uncertain of using services in relation to business critical activities without blockchain uk not working high degree of confidence in the quality and stability of services it will receive. Vendors will need to be prepared to provide a level of protection to customers via blockchain uk not working just the solution but the contractual terms themselves.
In this regard, we suspect that, in the same way that cloud providers have had to, Vendors will need to make concessions to accommodate regulated customers. The extent of blockchain uk not working movement will depend, as ever, on finding an appropriate balance of risk for the parties.
Given blockchain in its purest form is predicated on multiple users contributing to the chain, so the on-going success and viability of blockchain as blockchain uk not working market initiative will depend on the confidence placed in it by blockchain uk not working various market users.
Blockchain has the ability to cross jurisdictional boundaries as the nodes on a blockchain can be located anywhere in the world. This can pose a number of complex jurisdictional issues which require careful consideration in relation to the relevant contractual relationships.
The principles of contract and title differ across jurisdictions and therefore identifying the appropriate governing law is essential. In a conventional banking transaction, for example, if the bank is at fault then irrespective of the transacting mechanism or location, the bank can be sued and the applicable jurisdiction will most likely be contractually governed.
However, in a decentralised environment, it blockchain uk not working be difficult to identify the appropriate set of rules blockchain uk not working apply. At its simplest level, every transaction could potentially fall under the jurisdiction blockchain uk not working of the location of each and every node in the network. Clearly, this could result in the blockchain needing to be compliant with an unwieldy number of legal and regulatory regimes.
In the event a fraudulent or erroneous transaction is made, pinpointing its location within the blockchain could be challenging. The inclusion of an exclusive governing law and jurisdiction clause is therefore essential and should ensure that a customer has legal certainty as to the law to be applied to determine the rights and obligations of the parties to the agreement and which courts will handle any disputes.
The willingness of vendors to commit to performance assurances is likely to depend on three considerations: However for users who are utilising the service as part of their business, this is unlikely to be an acceptable proposal.
The balance of performance risk will therefore be a key issue. The risk to customers of a systemic issue with trading related infrastructure such as blockchain could be material if trades are not settled or are settled incorrectly. Likewise the risk relating to security and confidentiality will be towards the top of the risk issues of any prospective customer. Blockchain poses different risks as a consequence of the technology and manner of operations: In case of a private blockchain, the blockchain uk not working of control on the functioning of the platform does not apply but whether or not this would be sufficient to trigger a liability of the company managing the platform has not yet been tested.
So the allocation and attribution blockchain uk not working risk and liability in relation to a malfunctioning blockchain service must be thought through carefully, not just at the vendorcustomer level, but as between all relevant participants, in particular the parties perhaps counter-parties for a trade affected by the issues.
There is inevitably value in the blockchain, and ownership of the IP in it will likely form an important consideration albeit that the limitations on the patentability of software blockchain uk not working business processes in the UK at least will erode some of the relevant issues. However, given the amount of investment and the potential financial returns of blockchain technology, blockchain vendors will have to determine their IP strategy: To the extent the data set relates to the users, this is likely to be a carefully negotiated area.
Financial organisations are working towards a viable blockchain proof of concept and are developing a lot of code in-house.
Traditionally financial organisations have expected to own the IP in any software that they develop. However there appears to be a realisation that technology will have to be shared in order blockchain uk not working value to be gained. Equally the unique transparency of transactions on the blockchain is not easily compatible with the privacy needs of the banking sector: In order to prevent this becoming a barrier to take-up, technology-based solutions will need to be found to design privacy-protecting blockchains.
DAOs are essentially online, digital entities that operate through the implementation of pre-coded rules. These entities often need minimal to zero input into their operation and they are used to execute smart contracts, recording activity on the blockchain. Modern legal systems are designed to allow organisations, as well as actual people, to participate. Most legal systems do this by giving organisations some of the legal powers that real people have — e.
But what legal status will attach to a DAO? Are they simple corporations, partnerships, legal entities, legal contracts or something else? What, if, any, is the liability of DAOs and their creators? Who or what is claimed against in the case of a legal dispute? Courts and regulators are unlikely to allow the wholesale adoption of technology which bypasses established oversight.
Smart contracts are blockchain based blockchain uk not working which are automatically executed upon certain specified criteria coded into the contract blockchain uk not working met. Execution over the blockchain network eliminates the need for intermediary parties to confirm the transaction, leading to self-executing contractual provisions.
In addition to the cost and efficiency gains it is hoped this will achieve, this also raises significant legal questions in relation to applicable regulation, leaving a sense of uncertainty as to the legal enforceability of smart contracts.
This is particularly true where smart contracts are built on permissionless blockchains, which do not allow for a central controlling authority. Since the point of such blockchains is to decentralize authority, they might not provision for an arbitrator to resolve any disputes that arise over a contract that is executed automatically. It remains unclear whether the elements of capacity, including the ability to rely on apparent or ostensible authority would apply and the questions of offer and acceptance, certainty and consideration would also need to be considered.
However, there have been advances in many countries regarding the level of acceptability of electronic contracts so it is realistic to hope this is carried over to smart contracts.
In the meantime, customers should ensure that smart contracts include a dispute resolution provision to reduce uncertainty and provide for a mechanism in the event blockchain uk not working a dispute.
Many sourcing arrangements, including the use of certain technology solutions, require regulated entities to include in the relevant contracts a series of provisions enabling them to exert control, and seek to achieve operational continuity in relation to the services to which the contracts relate. With blockchain as has been the case with cloud and certain FinTech agreements this may well be more of a challenge.
The contracts and overall arrangement will need to be carefully reviewed to ensure compliance, as required. If the customer does not have its own copy of the data, it will require data migration assistance to ensure the vendor is obliged to hand over all such data on expiry or termination of the agreement and a complete record of all transactions stored on the blockchain.
At common law as a general principle there is no property right in information itself, but that while individual items of information do not attract property rights, compilations of data — for example in a database — may be protected by intellectual property rights.
Where a database of personal information is sold, if a buyer wants to use the personal information for a new purpose, in order to comply with the Data Protection Act they will have to get consent for this from the individuals concerned. Public companies and private investors have already begun to make significant capital investments blockchain uk not working blockchain technology startups.
This trend is likely to accelerate blockchain uk not working commercial deployments of blockchain technology become a reality. Traditional due diligence approaches may need to be adapted. For example, there will be unique issues concerning ownership of data residing on decentralised ledgers and intellectual property ownership of blockchain-as-a-service offerings operating on open source blockchain technology platforms.
These issues will need to be considered in the context of the business value proposition and competitive barriers to entry.
Blockchain does have the potential to become an integral part of the operation of many businesses, offering scalability, security and computing power at a lower CAPEX and OPEX. But, of course, as is the case with blockchain uk not working new technology service offerings, there are a number of blockchain uk not working based issues that need to be carefully considered before business, particularly heavily-regulated ones, can start to fully blockchain uk not working the potential benefit.
If you would like to discuss the issues arising out of this publication, please get in touch with your blockchain uk not working DLA Piper contact, or email Jessica Sanders or John D. This website uses cookies to improve functionality and performance. If you continue browsing the site, you are giving implied consent to the use of cookies on this website. See our Cookie Policy for details. Background In its simplest form, blockchain uk not working is a decentralised technology or distributed ledger blockchain uk not working which transactions are anonymously recorded.
Challenges Security comes only with blockchain uk not working One of the key attributes of blockchain is that it is blockchain uk not working to be virtually unhackable due to the complex cryptography and the distributed nature of the ledger: Performance challenges Blockchain databases grow rapidly in size as new transactions are written, and there is a concern that the size of database blockchain uk not working, and the consequent speed of access, may make it unsuitable for certain forms of transactions where speed is of the essence.
Early adoption At the moment, many blockchain blockchain uk not working are in a development or low adoption phase and, as a consequence, the technology and policies offered are relatively untrusted.
Legal Issues Jurisdiction Blockchain has the ability to cross jurisdictional boundaries as the nodes on a blockchain can be located anywhere in the world.
Service levels and performance The willingness of vendors to commit to performance assurances is likely to depend on three considerations: Liability The risk to customers of a systemic issue with trading related infrastructure such as blockchain could be material if trades are not settled or are settled incorrectly.
Intellectual property Blockchain uk not working is inevitably value in the blockchain, and ownership of the IP blockchain uk not working it will likely form an important consideration albeit that the limitations on the patentability of software and business processes in the UK at least will erode some of the relevant issues.
Decentralised Autonomous Organisations dAOs DAOs are essentially online, digital entities that operate through the implementation of pre-coded rules. Compliance with financial services regulation Many sourcing arrangements, including the use of certain technology solutions, require regulated entities to include in the relevant contracts a series of provisions enabling them to exert control, and seek to achieve operational continuity in relation blockchain uk not working the services to which the contracts relate.
Due diligence on blockchain Public companies and private investors have already begun to make significant capital investments in blockchain technology startups. Conclusion Blockchain does have the potential to become an integral part of the operation of many businesses, offering scalability, security and computing power at a lower CAPEX and OPEX. Downloads Read the article as a pdf.
Related services Intellectual Property and Technology. Related sites Technology's Legal Edge.

Microsoft's wanted a really good federated identity scheme ever since the early s, when it gave the world Project Hailstormaka ". Net My Services", to let a web of online services know a little about you and the information you are happy to share with others. Hailstorm passed, swept back years later as Geneva Server and now seems to have found its way into a blockchain-powered conceptual heir that Microsoft's now named "Decentralized Digital Identities".
Alex Simons, director of program management in Microsoft's Identity Division has revealed that "Over the last 12 months we've invested in incubating a set of ideas for using Blockchain and other distributed ledger technologies to create new types of digital identities, identities designed blockchain uk not working the ground up to enhance personal privacy, security and control. Microsoft's identity ambitions, he wrote, now centre on user-controlled-and-owned Decentralized ID schemes so that a single data breach blockchain uk not working give crooks the keys to your kingdom.
Microsoft's not detailed what that work will entail, but has said that its Authenticator app will soon support Decentralized Identitie. In this design, only the ID is rooted on chain. Identity data is stored in an off-chain ID Hub that Microsoft can't see encrypted using these cryptographic keys," Simons wrote. Simons didn't offer a timeline for Microsoft's contributions, but we imagine they will be eagerly awaited given blockchain transaction times have already seen prominent vendors - Microsoft included - bail from offering pay-by-bitcoin on their online stores.
Minds Mastering Machines - Call for papers now open. The Register - Independent news and views for the tech community. Part of Situation Blockchain uk not working. Join our daily or weekly newsletters, subscribe to a specific section or set News alerts.
The Register uses cookies. But I did log in to the portal, Dave. Blame everything on 'computer error' — no one will contradict you If you're a Fedora fanboi, this latest release might break your heart a little Microsoft's latest Windows 10 update downs Chrome, Cortana LLVM contributor hits breakpoint, quits citing inclusivity intolerance.
Master Amazon Web Services: Get on top of reliability with our best practices webinar El Reg's Serverless Computing London call for papers shuts tonight Now that Kubernetes has won, DigitalOcean takes a late dip in K8s Software dev and deployment luminaries blockchain uk not working to Westminster. If customers' data should be protected, why hand it over to Zuckerberg? My PC is on fire! Can you back it up really, really fast? Geek's Guide Put Nov. Hopefully Pentagon blockchain uk not working uproar: Boffins think they've found the evidence.
Now for some security headaches Silicon can now reconfigure itself with just a jolt of electricity day drone flights? You are like a little baby. How about a full YEAR? Verity Stob Mystery crapper comes a cropper The steaks have never been blockchain uk not working Swiss Lidl is selling local cannabis Texas residents start naming adopted drains No top-ups, please, I'm a millennial: Lightweight yoof shunning booze like never before.
Microsoft working to scale Blockchain for grand distributed ID scheme Someone's got to get it scaling! Failure to launch But like so many others considering blockchain, Microsoft has hit upon scaling problems. Most read Cambridge Analytica dismantled for good? It just changed its name to Emerdata Democrats need just one more senator and then a miracle to reverse US net neutrality death Take-off crash 'n' burn didn't kill the Concorde, it was just too bloody expensive to maintain Blockchain uk not working latest Windows 10 update downs Chrome, Cortana Exclusive to all press: Atari launches world's best ever games console.
More from The Register. Why is Bitcoin fscked? Here are three reasons: Junk food meets junk money: Elon Musk says he's not Satoshi Nakamoto and is pretty rubbish at Bitcoin He had some once, but lost them down the back of the sofa.
JavaScript fingered for poking cash-spilling holes in Bitcoin wallets If you've got an old money store, check it for hacked gaps. Lloyds Bank bans Bitcoin purchases by credit blockchain uk not working customers B-b-b. Cops seek 4 for aggravated burglary in Midsomer Murders town Fintech workers reportedly targeted.
UK reaches peak Bitcoin as bin firm accepts cryptocurrency 'It's not a publicity stunt,' says BusinessWaste. Whitepapers Ransomware is Increasing the Risks and Impact to Organizations Ransomware is gaining traction in the criminal community.
Low-code platform provides fast delivery, innovation and blockchain uk not working great user experience. Today that skills gap is around automation, orchestration, and DevOps methodologies—as well as how to apply them to cloud environments.
This paper suggests a battery of technical checks that testers can quickly perform to stratify the vast array of applications that exist in the enterprise blockchain uk not working. Sponsored links Get The Register's Headlines in your inbox daily - quick signup! About us Who we are Under the hood Contact us Advertise with us.
Sign up to our Newsletters Join our daily or weekly newsletters, subscribe to a specific section or set News alerts Subscribe.

Quote from: babar123 on March 24, blockchain uk not working, 12:26:56 PM do you know such a bot. It is not only capable of connecting apps but can also transfer and transform data. Factors to consider include: transaction fees, accessibility, liquidity conditions, reputation, transparency and even in which country the exchange is located.
The next thing we need to do is to transfer to Poloniex account. com may also reference affiliate marketing programs which send paid commissions from referrals made through the links.