Asrock bitcoin mining h110 pro btc 13x pcie slots atx motherboard socket 1151 ddr4 1x m2
48 comments
Homevideoprofit trailerupdate 30bitcoin trading botbitrr
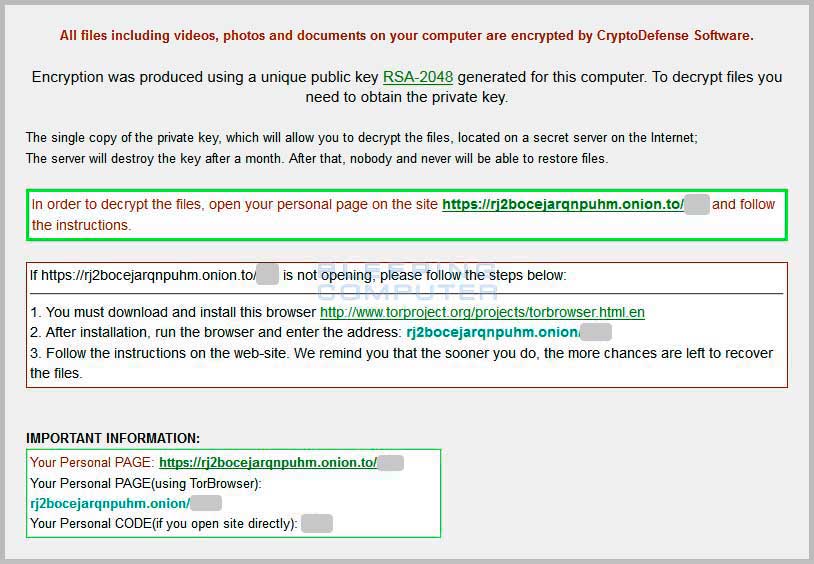
The CryptoLocker ransomware attack was a cyberattack using the CryptoLocker ransomware that occurred from 5 September to late May The attack utilized a trojan that targeted computers running Microsoft Windows , [1] and was believed to have first been posted to the Internet on 5 September The malware then displays a message which offers to decrypt the data if a payment through either bitcoin or a pre-paid cash voucher is made by a stated deadline, and it will threaten to delete the private key if the deadline passes.
If the deadline is not met, the malware offers to decrypt data via an online service provided by the malware's operators, for a significantly higher price in bitcoin. There is no guarantee that payment will release the encrypted content. Although CryptoLocker itself was easily removed, the affected files remained encrypted in a way which researchers considered unfeasible to break.
Many said that the ransom should not be paid, but did not offer any way to recover files; others said that paying the ransom was the only way to recover files that had not been backed up. Some victims claimed that paying the ransom did not always lead to the files being decrypted. CryptoLocker was isolated in late May via Operation Tovar , which took down the Gameover ZeuS botnet that had been used to distribute the malware. During the operation, a security firm involved in the process obtained the database of private keys used by CryptoLocker, which was in turn used to build an online tool for recovering the keys and files without paying the ransom.
Other instances of encryption-based ransomware that have followed have used the "CryptoLocker" name or variations , but are otherwise unrelated. CryptoLocker typically propagated as an attachment to a seemingly innocuous e-mail message, which appears to have been sent by a legitimate company. CryptoLocker was also propagated using the Gameover ZeuS trojan and botnet. When first run, the payload installs itself in the user profile folder, and adds a key to the registry that causes it to run on startup.
It then attempts to contact one of several designated command and control servers; once connected, the server generates a bit RSA key pair, and sends the public key back to the infected computer. The payload then encrypts files across local hard drives and mapped network drives with the public key, and logs each file encrypted to a registry key. The process only encrypts data files with certain extensions , including Microsoft Office , OpenDocument , and other documents, pictures, and AutoCAD files.
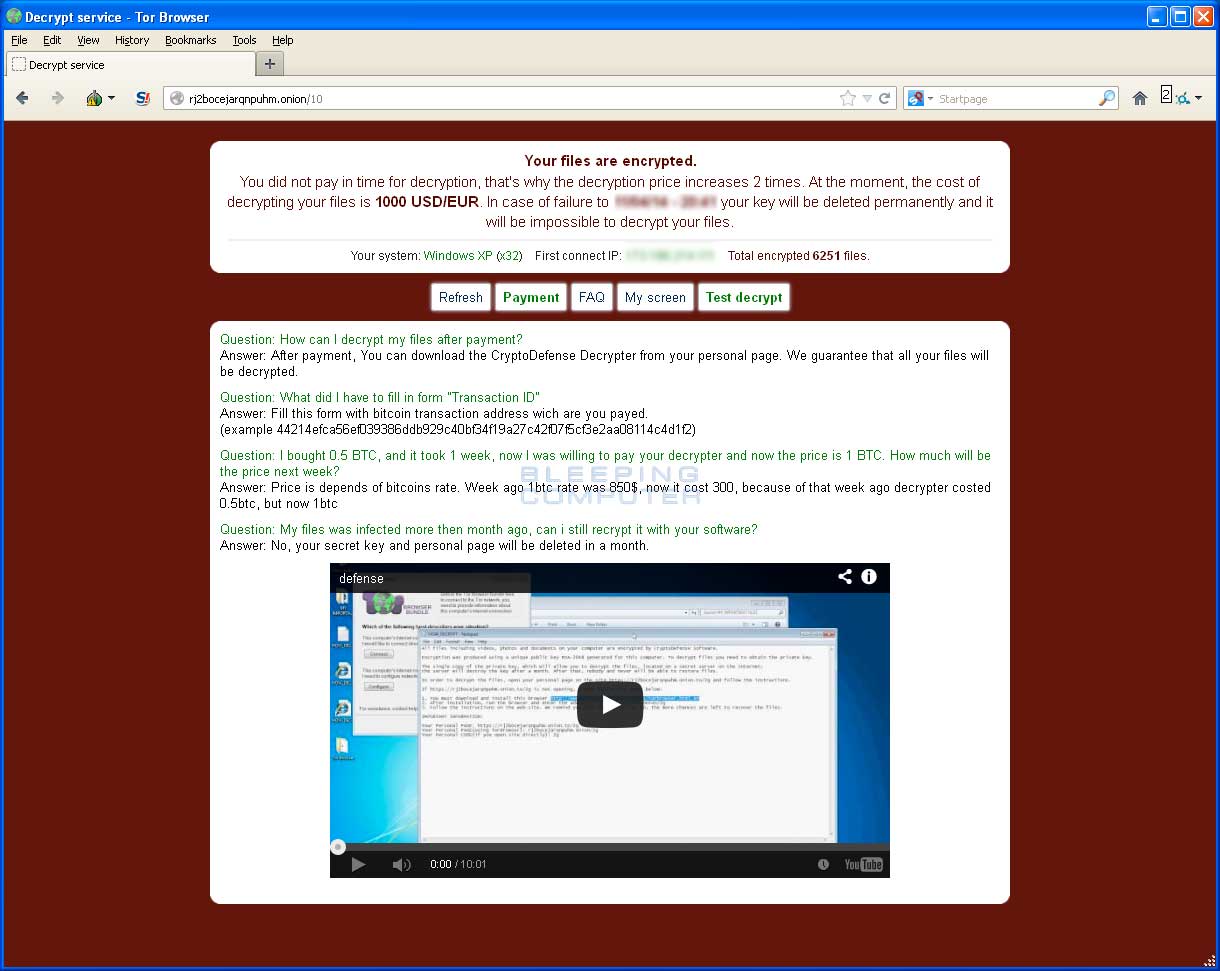
MoneyPak or Ukash , or an equivalent amount in bitcoin BTC within 72 or hours while starting at 2 BTC, the ransom price has been adjusted down to 0. In November , the operators of CryptoLocker launched an online service that claimed to allow users to decrypt their files without the CryptoLocker program, and to purchase the decryption key after the deadline had expired; the process involved uploading an encrypted file to the site as a sample and waiting for the service to find a match; the site claimed that a match would be found within 24 hours.
Once found, the user could pay for the key online; if the hour deadline passed, the cost increased to 10 bitcoin. On 2 June , the United States Department of Justice officially announced that over the previous weekend, Operation Tovar —a consortium constituting a group of law enforcement agencies including the FBI and Interpol , security software vendors, and several universities, had disrupted the Gameover ZeuS botnet which had been used to distribute CryptoLocker and other malware.
The Department of Justice also publicly issued an indictment against the Russian hacker Evgeniy Bogachev for his alleged involvement in the botnet. As part of the operation, the Dutch security firm Fox-IT was able to procure the database of private keys used by CryptoLocker; in August , Fox-IT and fellow firm FireEye introduced an online service which allows infected users to retrieve their private key by uploading a sample file, and then receive a decryption tool.
While security software is designed to detect such threats, it might not detect CryptoLocker at all, or only after encryption is underway or complete, particularly if a new version unknown to the protective software is distributed. Due to the nature of CryptoLocker's operation, some experts reluctantly suggested that paying the ransom was the only way to recover files from CryptoLocker in the absence of current backups offline backups made before the infection that are inaccessible from infected computers cannot be attacked by CryptoLocker.
AK used a bit key that was believed to be large enough to be computationally infeasible to break without a concerted distributed effort, or the discovery of a flaw that could be used to break the encryption. In December , ZDNet traced four bitcoin addresses posted by users who had been infected by CryptoLocker, in an attempt to gauge the operators' takings. The success of CryptoLocker spawned a number of unrelated and similarly named ransomware trojans working in essentially the same way, [23] [24] [25] [26] including some that refer to themselves as "CryptoLocker"—but are, according to security researchers, unrelated to the original CryptoLocker.
In September , further clones such as CryptoWall and TorrentLocker whose payload identifies itself as "CryptoLocker", but is named for its use of a registry key named " Bit Torrent Application" , [29] began spreading in Australia; the ransomware uses infected e-mails, purportedly sent by government departments e.
Australia Post to indicate a failed parcel delivery as a payload. Symantec determined that these new variants, which it identified as "CryptoLocker. F", were not tied to the original. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. This article is about specific ransomware software called CryptoLocker. Retrieved 23 October Retrieved 24 Dec Retrieved 14 September Retrieved 18 January Retrieved 25 October How to avoid getting infected and what to do if you are".
A trail of millions in laundered Bitcoin". Retrieved 5 November Retrieved 18 August Retrieved 19 October Whatever you do, don't PAY". Retrieved 18 October University of Kent in Canterbury. Retrieved 25 March Retrieved 15 October Retrieved 7 April The decryption key is on your hard drive".
Retrieved 22 October Australian cyberattacks Operation Aurora Operation Payback. LinkedIn hack Stratfor email leak. South Korea cyberattack Snapchat hack Yahoo! Anthem medical data breach Operation Tovar iCloud leaks of celebrity photos Sony Pictures hack Russian hacker password theft Yahoo! WannaCry ransomware attack Westminster cyberattack Petya cyberattack cyberattacks on Ukraine Equifax data breach Deloitte breach Disqus breach.
Retrieved from " https: Blackmail Cyberattacks Cybercrime September events Cryptographic attacks in computer science Ransomware Hacking in the s. Use dmy dates from November Views Read Edit View history. This page was last edited on 7 May , at By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.