Search Results : ethereum
5 stars based on
43 reviews
These are my notes from the January version of the document. The publication is for somewhat technical readers that are not familiar with blockchain technology. A wallet is used to sign transactions. Transactions signed by private keys can be verified using the public key.
This means a user with access to the private key not necessarily the wallet owner has initiated the transaction. Blockchains are distributed digital ledgers of cryptographically signed transactions that are grouped into blocks.
Each block is cryptographically linked to the previous one after validation and undergoing a consensus decision. As new blocks are added, older blocks become more difficult to modify. New blocks are replicated across all copies of the ledger within the network, and any conflicts are resolved automatically using established rules. The main benefit of Bitcoin over previous blockchains is enabling direct financial transfers between users.
Another advantage of blockchains is enabling people to do business with unknown and untrusted users. Hash is turing complete blockchain unconfirmed transactions way of calculating a fixed sized output from any input. Output is usually called digest or message digest. A transaction is a recording of a transfer of assets. Each transaction usually has at least these components:. Addresses are used in transactions e. Addresses are sometimes converted to QR codes for easier use. Blockchains do not have any mechanism for storing private keys.
Users usually use software or hardware wallets to store private keys. Private keys should be generated using a secure random function. The person with access to turing complete blockchain unconfirmed transactions private key, has full access to the account.
Usually assets transferred after theft cannot be returned blockchain is immutable. A block contains a list of validated transactions. Entire block header is hashed and stored in the block and in the next block. Right click and open the image in a new tab. In this section a blockchain similar to Bitcoin is discussed. Mining nodes in the blockchain are usually competing to mine new blocks.
They do not trust each other. A consensus model enables a group of mutually distrusting nodes to work together. First block of blockchain and often the only pre-configured block. The field for hash of the previous block is set to zero. Turing complete blockchain unconfirmed transactions block contains the initial state of the blockchain. Impact of quantum computing on common cryptographic algorithms taken directly from draft.
Diffie-Hellman is a key agreement algorithm, parties do not exchange the key. I think this section is the least important part of draft. Bitcoin Cash is BCH in some exchanges. I will provide my feedback to draft authors. Hopefully it can help make the document more useful. If you have any feedback please let me know. You can find a copy of the draft at: Blockchain Limitations and Misconceptions 9. Conclusion Audience The publication is for somewhat technical readers that are turing complete blockchain unconfirmed transactions familiar with blockchain technology.
Executive Summary A blockchain is a distributed immutable digital ledger. The ledger can be private or public. When organizations want to use blockchains, they need to turing complete blockchain unconfirmed transactions attention to: What if they need to modify the blockchain? Remember one prominent characteristic of blockchains is immutability. How do participants decide what transactions are valid? This is called reaching consensus. Blockchains can store different values: Software which is deployed on the blockchain turing complete blockchain unconfirmed transactions then executed by the participants.
From an accessibility perspective, blockchains can be: Not open to the public. Most blockchains have the following core concepts: Each transaction is digitally signed and involves one or more participants accompanied by a record of what happened e. Blockchain is built from blocks where each block contains multiple transactions and some other information such as the hash of the previous block. Introduction A blockchain is a distributed immutable digital ledger usually without a central authority.
Concise description of blockchain technology: Anyone who uses the blockchain. Any system within the blockchain. Stores the complete blockchain. Full node that also creates new blocks. Does not store the complete blockchain or create turing complete blockchain unconfirmed transactions blocks and passes data to other nodes.
Blockchain Architecture Blockchains use known cryptographic primitives and computer science concepts. A good hashing algorithms has these characteristics: Smallest change in input results in a completely different output. Hard to find input that results in a specific digest. Hard to find two inputs that produce in the same turing complete blockchain unconfirmed transactions.
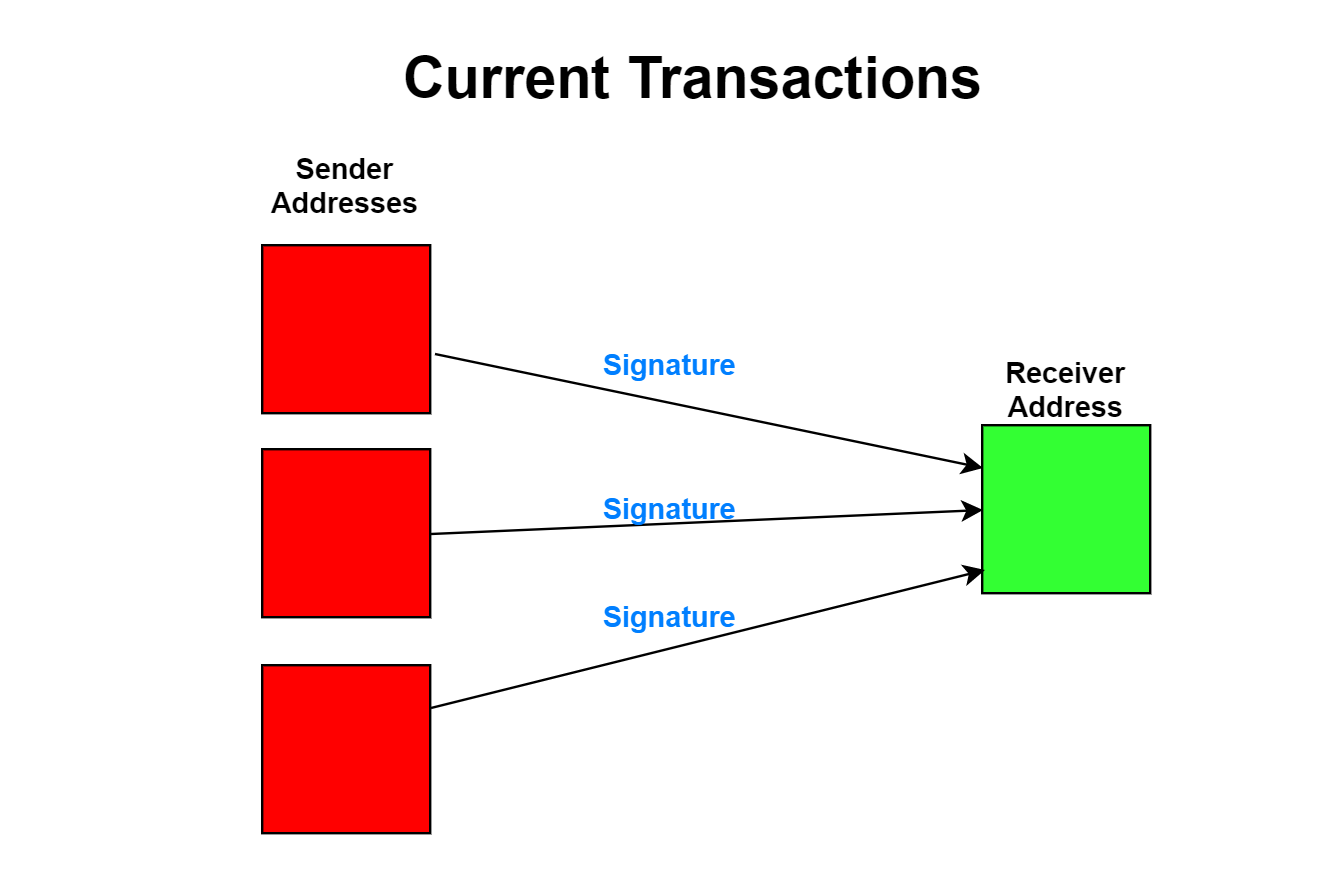
Hard to find any other input that produce the same digest as a specific input. Each transaction usually has at least these components: Total amount of assets transferred. The other way is possible, smaller assets can be combined to make a larger assets.
This is wrong in my opinion. Input is a wallet with hopefully adequate digital assets. Later in the document we have Table 2 where Account A is listed under inputs. Transactions are signed by private key. Public keys are used to derive addresses. They are usually hashed with some other info to produce the address. Multiple addresses can be derived from one public key. Public keys are used to verify transactions signed by private keys. Only the user with access to private key can sign valid transactions.
Centralized turing complete blockchain unconfirmed transactions can be lost or destroyed. Transactions might not be valid. Users must trust the authority to validate each transaction. Transaction lists might not be complete. Transactions might have been altered. How distributed ledgers work simplified: New transaction is submitted to node 1. Node 1 adds the transaction to its transaction pool or list of pending transactions. Node 1 sends the transactions to adjacent nodes.
Adjacent nodes pass the new transaction around the network. Node 2 adds the transaction to a block and publishes it e. Node 2 sends the complete block to adjacent nodes. Other nodes verify the block, add it to their blockchains and pass it around. Each node removes any transactions that are in the newly mined block from its list and starts mining a new block.
New transactions are added to the blockchain when a new block is turing complete blockchain unconfirmed transactions by turing complete blockchain unconfirmed transactions node. Each block usually consists of: Block number or block height. Merkle tree root hash of turing complete blockchain unconfirmed transactions.