Ctsv intercooler core liquid aftermarket
49 comments
Cara membuat robot status bbm berwarna biru diamond
An initial coin offering ICO or initial currency offering derived form initial public offering is a means of crowdfunding centered around cryptocurrency , [1] [2] which can be a source of capital for startup companies.
These tokens are promoted as future functional units of currency if or when the ICO's funding goal is met and the project launches. ICOs provide a means by which startups avoid costs of regulatory compliance and intermediaries, such as venture capitalists, bank and stock exchanges, [4] while increasing risk for investors. ICOs may fall outside existing regulations [5] [6] depending on the nature of the project, or are banned altogether in some jurisdictions, such as China and South Korea.
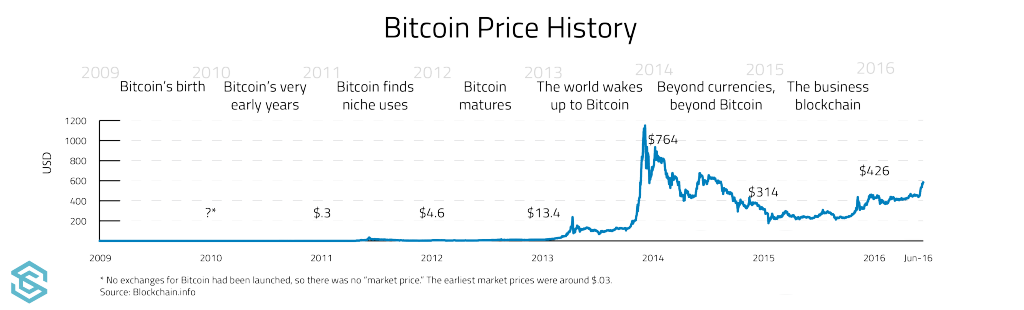
Almost half of ICOs sold in failed by February ICOs and token sales became popular in There were at least 18 websites tracking ICOs before mid-year. In connection with this ICO, an unidentified third party executed a phishing scam by circulating a fake URL for the offering through social media.
By the end of , ICOs had raised almost 40 times as much capital as they had raised in , although still amounting to less than two percent of the capital raised by IPOs. ICOs are sometimes called " token sales ". Amy Wan, a crowdfunding and syndication lawyer, described the coin in an ICO as "a symbol of ownership interest in an enterprise—a digital stock certificate" stating that they are likely subject to regulation as securities in the U.
Tokens are generally based on the Ethereum ERC20 standard. On January 30, , Facebook banned advertisements for ICOs as well as for cryptocurrencies and binary options. ICOs can be used for fraud, as well as legal activities such as corporate finance and charitable fundraising. Securities and Exchange Commission SEC has warned investors to beware of scammers using ICOs to execute " pump and dump " schemes, in which the scammer talks up the value of an ICO in order to generate interest and drive up the value of the coins, and then quickly "dumps" the coins for a profit.
The developers themselves can be guilty of such tactics. Facebook has banned ICO and cryptocurrency advertisements on its platform stating that many of them were "not currently operating in good faith. The Japanese platform Line and the Russian platform Yandex have similar prohibitions. Even in cases of legitimate ICOs, funded projects are typically in an early and therefore high-risk stage of development.
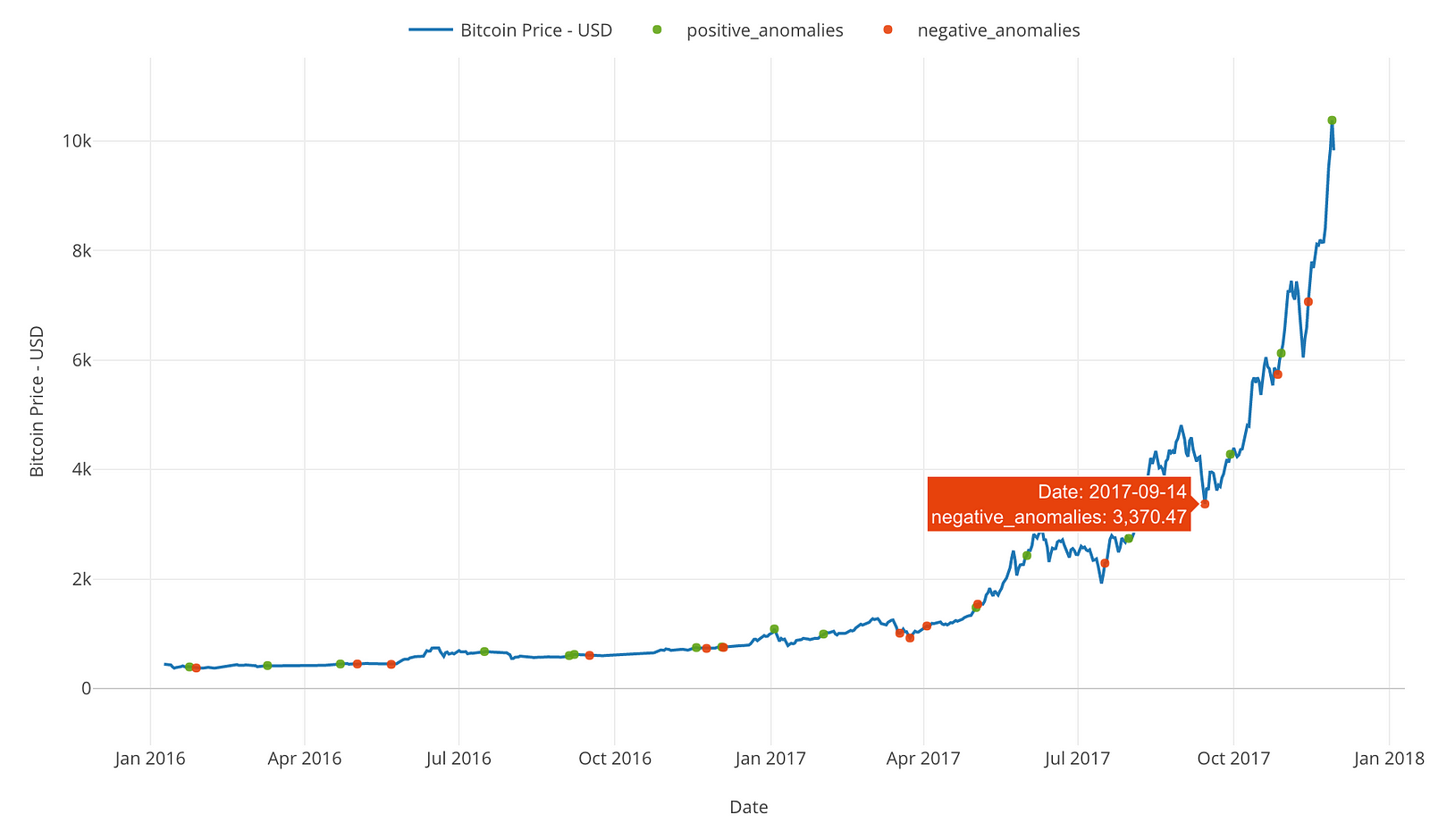
A Wired article predicted in that the bubble was about to burst. Following a speculative boom in cryptocurrency prices that peaked in December , regulation of cryptocurrencies has been rapidly changing. The pace of change has been driven in part by incidents of cybertheft, trading halts, and possible market manipulation.
Cryptocurrencies are based on distributed ledger technologies which enable anyone to purchase or transfer their cryptocurrency holdings to any other person without the need for an intermediary such as an exchange or to update a central record of ownership. Cryptocurrencies can be transferred easily across national and jurisdictional boundaries. Countries have different approaches to how they regulate cryptocurrencies.
This can depend on the nature of the cryptocurrency itself. There are two main types of cryptocurrencies from a regulatory perspective: Utility tokens may have value because they enable the holder to exchange the token for a good or service in the future, such as Bitcoin. Asset-backed tokens may have value because there is an underlying asset which the holder of the token can attribute value to.
In many countries it is uncertain whether utility tokens require regulation, but it is more likely that asset-backed tokens do require regulation.
This makes it complex for the issuers of cryptocurrencies to analyse which countries their tokens or coins can be sold into, and for the prospective purchasers of cryptocurrencies to understand which regulations, if any, should apply. The Gibraltar British Overseas Territory Financial Services Commission announced in early February that regulations are being developed to qualify "authorized sponsors" of ICOs, who are supposed to be "responsible for assuring compliance with disclosure" and compliance with "financial crimes rules".
The company had drawn endorsements from celebrities including Floyd Mayweather Jr. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Risks, Regulation, and Accountability". Regulation of Financial Institutions Journal. Notes on the 21st Century. Retrieved 8 February The Concise Fintech Compendium.
Retrieved May 4, Retrieved 27 July The Wall Street Journal. Retrieved February 7, Retrieved April 2, Retrieved April 3, ICO fraud warning for investors from watchdog". Retrieved December 15, Retrieved April 4, Australian Securities and Investments Commission. Ministry of Industry and Information Technology. Securities and Futures Commission. Retrieved 15 December New Zealand Financial Markets Authority.
Retrieved 15 November The New York Times. Retrieved 3 November Proof-of-authority Proof-of-space Proof-of-stake proof-of-work. Dogecoin Gulden Litecoin PotCoin. Dash Decred Primecoin Auroracoin. IO Gridcoin Nxt Waves. Anonymous Internet banking Bitcoin network Complementary currency Crypto-anarchism Cryptocurrency exchange Digital currency Double-spending Electronic money Initial coin offering Airdrop Virtual currency.
Retrieved from " https: Wikipedia indefinitely semi-protected pages All articles with unsourced statements Articles with unsourced statements from May All articles with failed verification Articles with failed verification from March Views Read View source View history. This page was last edited on 5 May , at By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.
Working on regulating ICOs. On September 4, seven Chinese financial regulators officially banned all ICOs within the People's Republic of China, demanding that the proceeds from all past ICOs be refunded to investors or face being "severely punished according to the law". The Securities and Futures Commission released a statement in September explaining that tokens may constitute securities for purposes of the Securities and Futures Ordinance, in which case dealing in such tokens would be a regulated activity under Hong Kong law.
In October , the government of Gibraltar established a framework for regulating distributed ledger technology DLT companies, which came into law on January 1, It encompasses ICOs and subjects them to financial controls and standards. Although Switzerland was previously viewed as a friendly jurisdiction to coin offerings, the Swiss Financial Market Supervisory Authority announced an investigation of an unspecified number of coin offerings in September , and would examine whether these offerings were in compliance with Swiss regulations.
In July the U.