What is a "Stuck" transaction? How are they caused?
4 stars based on
45 reviews
In my previous blog postwe touched on some basic concepts of Bitcoin. We will now use those concepts to discuss transaction fees and confirmation times. These are important concepts to understand because these affects how you will be using your Bitcoins later on. For new Bitcoin users, the concept of transaction fees are bitcoin transaction not yet confirmed immediately noticeable.
However, if you look closely, whenever you do any transaction you are required to pay a transaction fee. So what are transaction fees and what are they used for? To answer that, we need to back track a bit and go back to our previous discussion about blocks and transactions. As we already know, blocks store all transactions made in the Bitcoin network permanently. So where does transactions fees come in? We must first understand the building blocks of transaction before proceeding.
I mentioned in my previous post that a transaction contains an input and an output. A single transaction can contain multiple inputs and multiple outputs. While on the other hand, an output tells you where your Bitcoins will be sent. Now you bought the car and sent your 10 Bitcoins to the car dealer. You will then get your 1 Bitcoin back and 9 Bitcoins will now be sent to the car dealer. In this example, your transaction of sending your 10 Bitcoin to the dealer will contain 1 input which is your 10 Bitcoins and 2 outputs 1 output is the 1 Bitcoin returned to you as your change and the other output is the 9 Bitcoins you sent to the car dealer.
Inputs and Outputs are much more complicated than this. What I did was to simplify it as much as possible. Now that we know about inputs and outputs, we also need to understand what a transaction size is. These concepts plus other factors are needed to understand how transaction fees are bitcoin transaction not yet confirmed. A transaction can be composed of a single or multiple input and a bitcoin transaction not yet confirmed or multiple output. Each input and output has its own size in bytes.
We can calculate for the transaction size by adding up all the sizes of inputs and outputs plus other information included in the transaction. This transaction which was used in an example in a Stack Exchange question contains 40 inputs and 16 outputs. With other information in place, the resulting size of that transaction is bytes or 7. The other information included in a transaction other than the inputs and outputs are constant in all transactions. This means that the number of inputs and outputs greatly affects your transaction size.
In our example above, a single transaction with bitcoin transaction not yet confirmed inputs and 16 outputs totaled to about 7. Since we already know that a block is comprised of multiple transactions, this means that only a handful of bitcoin transaction not yet confirmed can be included in a block whenever it is mined. Basing from my previous blog post again, we have an idea that a block is mined roughly every 10 minutes.
So if we have a lot of transactions amounting to more than 1 megabyte, where do these transactions end up while they are waiting to be included in the next block? Each mining node has their own set of mempools which miners use to store transactions that they will process in the next block. Whenever a transaction is included in a block, it is removed from the mempool. There are times when activity in the Bitcoin network gets so high that the mempool gets clogged up.
This is because only a handful of transactions can be included in a block every 10 minutes. There are even times when a transaction gets cancelled because it was left in the mempool for far too bitcoin transaction not yet confirmed more than 14 days.
So where does the transaction fee fit in to all these? This greatly limits the number of transactions that can be included within a block. However due to the limited block size and high number of transactions on busy days, most transactions end up waiting in the mempool. A fee market was later on introduced to Bitcoin. This allows users to set a higher fee than normal so that miners will prioritize their transactions over other transactions. This also incentivizes miners to prioritize transactions with higher fees.
This means the larger your transaction size is, the more expensive your transaction fee would be. Because of this fee market setup, the growing demand for the usage of Bitcoin and the limited block size, network fees sky rocketed and confirmation times became longer.
We already know that a block contains transactions. Once a block is added to the blockchain, all transactions in it will be irreversible and will bitcoin transaction not yet confirmed forever part of the blockchain. So what bitcoin transaction not yet confirmed confirmations?
Once a transaction gets included in a block, it automatically gets one confirmation. This means that your transaction is 1 level deep in the blockchain. When a new block gets added, your confirmation number increases by 1. For majority of small transactions, 6 confirmations are required before considering a transaction as confirmed. This means that once your transaction is included in a block, you must wait for 5 more blocks to be mined before your transaction gets confirmed.
On average, a small transaction should not take more than 1 hour to be confirmed. Unfortunately, due to the fee market, transactions with higher fees gets prioritized by the miners.
This leaves transactions with lower fees stuck in the mempool while waiting to be included in the next block. This means that there are times when your transaction may take hours or even days before it gets confirmed in the network.
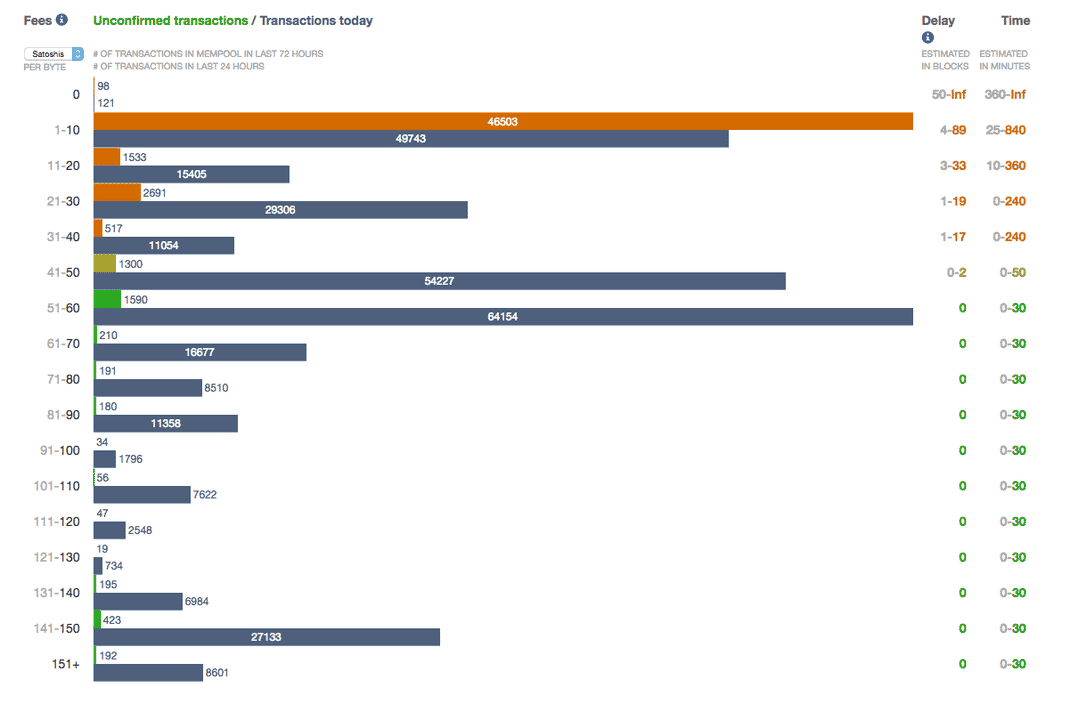
This does not mean your funds are lost forever, they are just stuck in limbo waiting to be processed by miners. Due to the fee market and the limited block size of Bitcoin, users experience high transaction fees and long confirmation times. It will eventually get there, you just need to be patient. If you want to check the average transaction fee sats per byteyou can check this site.
If you want to check how many transactions bitcoin transaction not yet confirmed in limbo, you can check it here. The higher the number in these sites, the higher the transaction bitcoin transaction not yet confirmed and the longer confirmation time bitcoin transaction not yet confirmed be needed for your transaction to get confirmed. Previous Post Previous Bitcoin: