Buy liquid phenobarbital for dogs
39 comments
Bitcoin handels software bot aktien handeln
Blockchain is a new technology to create a digital ledger of transactions maintained by a network of computers, obviating the need for the type of middlemen or centralized authorities that traditionally conduct, authorize or verify the transactions.
Its applications can go beyond mitigating fraud or lowering the cost of doing business. For example, blockchain is currently the technology behind the transactions of virtual currencies, most notably Bitcoin. It is an internet-based currency and its payment system requires no intermediaries for reconciliation and clearance.
Other virtual currencies in existence include Litecoin and Peercoin. They are commonly referred to as "cryptocurrencies". See Bank of England In trade finance, blockchain helps prevent duplicate financing of the same invoice by different banks.
The Steering Group released its report in February setting out its analysis and recommendations. Hong Kong has the potential to become a key blockchain technology hub through leveraging on its expertise in finance, logistics and other professional services.
This issue of Essentials aims to a describe the blockchain technology and its key features, b discuss its potential applications and initiatives being undertaken in the overseas financial markets, and c highlight the challenges of adopting the technology.
What is "blockchain" Blockchain is generally referred to as a database or digital ledger on which transactions are recorded. The term blockchain is derived from the two words "block" and "chain". An individual "block" refers to all of the transactions which have taken place within a fixed period of time.
Each block is "chained" to the next block mathematically and sequentially to form a blockchain. Given the latest block, it is possible to access previous blocks linked together in the chain. A blockchain database, thus, retains the complete history of all assets and instructions executed since the very first one - making its data verifiable and independently auditable.
This in turn allows blockchain to be used as a ledger which can be shared and corroborated by anyone with the appropriate permissions. As mentioned above, one of the key attributes of the blockchain technology is that it can eliminate the need for a central intermediary to verify and clear transactions.
The difference between the conventional approach and blockchain-based approach to transaction clearance is illustrated in Figure 1 below. In a blockchain network, each computer maintains an identical copy of the blockchain, which is updated automatically every time a new transaction takes place. Computers verify each transaction with sophisticated algorithms to confirm the transfer of value and other information and create a historical ledger of all valid activities.
The network computers that are processing the transactions are often spread across places and not owned or controlled by any single entity.
Since a blockchain is distributed in the network instead of being stored on a central server, it is sometimes referred to as a distributed ledger.
Figure 1 - Two different approaches to transaction clearance Sources: Such a decentralized system will likely consume more computing and network resources than a centralized system. As the size of the blockchain continues to grow with more data added, the resources required to operate the system may be more extensive and this draws concern whether the blockchain technology is suitable for large-scale applications;.
While a blockchain application can be operated by institutions in private networks, there are still issues over data privacy. For example, it may be possible to deduce a party's identity inappropriately based on the transactions or through access to a network user that has the permission to decrypt the data. For two decades there has been discussion about whether or not larger quantum computers could break public-key cryptographic systems, if and when they arrive with sufficient "qbits".
In addition, there are implications of moving an ever-growing chain of blocks around a distributed set of participants. The International Criminal Police Organization has cautioned that the blockchain technology currently utilized by virtual currencies is vulnerable to the cyber threat that malicious software and other illegal data may be embedded in the transactions and spread across the blockchain; 17 Legend symbol denoting See International Criminal Police Organization As pinpointed by the Financial Conduct Authority of the United Kingdom, innovation can be an iterative process and in order to give innovators "space" to develop their solutions, the Authority will not take a stance until the blockchain application is clearer.
It nevertheless recognizes that there are a lot of regulatory and consumer issues that will need to be addressed as the blockchain technology evolves. Indeed, successful application of the blockchain technology requires an effective regulatory regime to ensure that the technology is resilient to shocks or criminal activities. Bitcoin, being the first virtual currency, was launched in The important parts of a block are: Banks can use the blockchain technology to track the history of transactions with respect to the origin, ultimate destination and use of funds.
This helps improve the ability of banks to identify suspicious customers. Trade invoice financing allows a company to draw money against its sales invoices before the customer has actually paid, thereby improving its cash flow. Companies borrow from banks and financial institutions after furnishing unpaid customer invoices as collateral. Banks can only detect if the same invoice has been financed by themselves within a prescribed period of time, but they are not able to do so if the same invoice is financed by another bank.
By applying the blockchain technology, banks will have the ability to access a single source of information to detect if customers have obtained funding from multiple banks for the same invoices. For example, the trading order of participant A and participant B is matched on a securities exchange platform.
The blockchain-based system is able to verify that participant A owns the stock and participant B owns sufficient cash. The validated transaction is automatically recorded in the asset ledger and cash ledger respectively, eliminating the need for central clearing house. See Oliver Wyman NASDAQ Private Market enables companies to identify a pool of potential buyers and set parameters on the percentage of holdings that shareholders can sell.
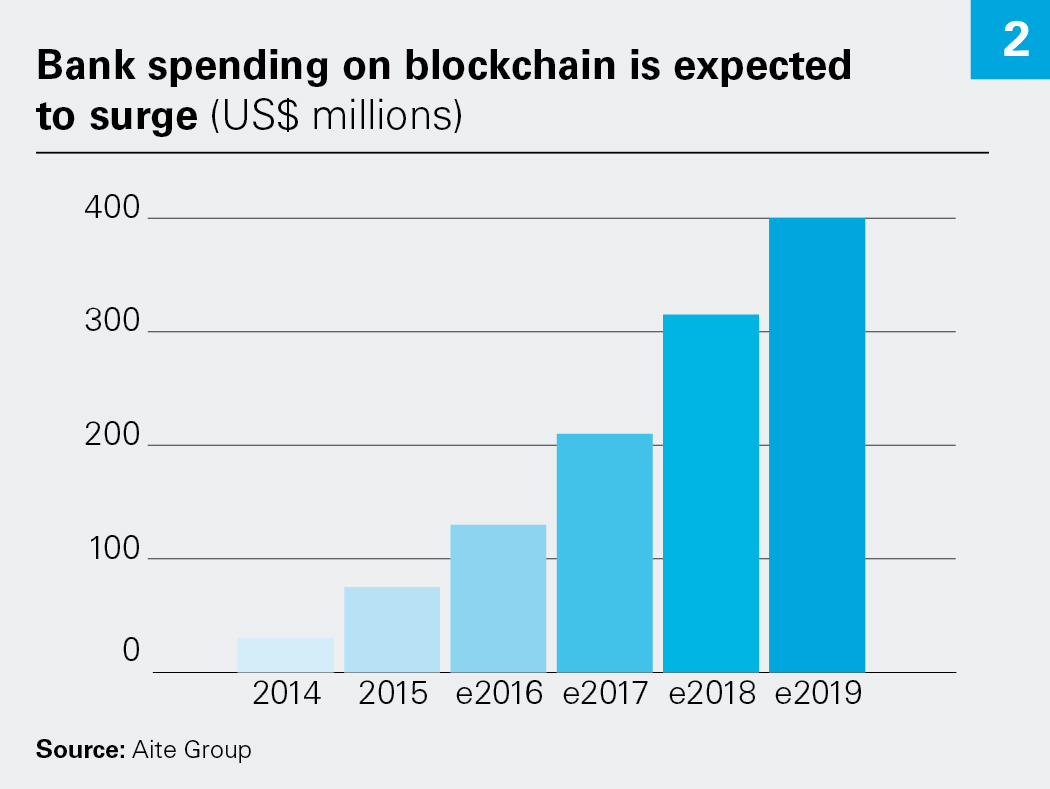
Participating shareholders gain liquidity, and the company is able to facilitate the transition of ownership into the hands of long-term institutional holders in advance of a public offering. See Aite Group According to Financial Conduct Authority , these issues include how individuals gain access to a distributed network, who have the right to control the process, and what data security exists for users.
Powering the Internet of Value. European Securities and Markets Authority. Speech by Verena Ross, Executive Director. Infocomm Development Authority of Singapore. International Criminal Police Organization. The Financial Times Technology: Banks seek the key to blockchain. UK Government Office for Science. Commodity Futures Trading Commission. Regulators and the Blockchain. The blockchain revolution in financial services.