Painful inner lip bite
4 stars based on
78 reviews
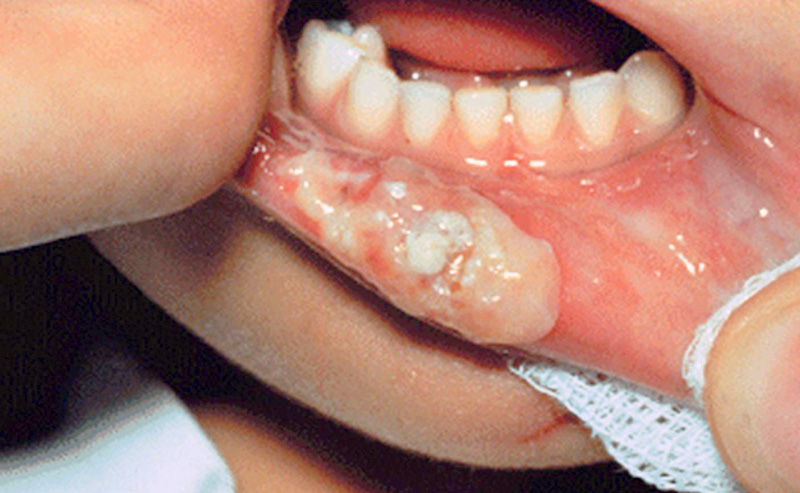
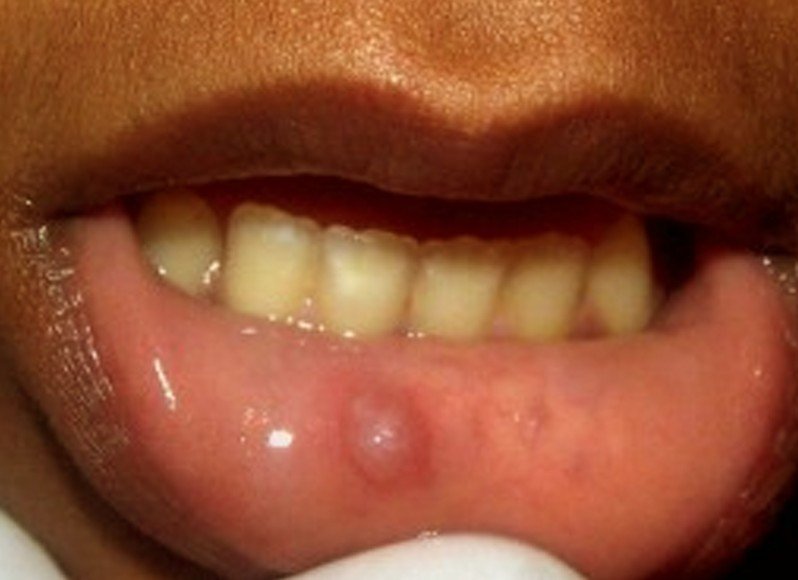
Morsicatio buccarum also termed chronic cheek biting and chronic cheek chewing is a condition characterized by bit inside lower lip irritation or injury to the buccal mucosa the lining of the inside of the cheek within the mouthcaused by repetitive chewing, biting or nibbling. Morsicatio buccarum is a type of frictional keratosis. The lesions are located on the mucosa, usually bilaterally in the central part of the anterior buccal mucosa and along the level of the occlusal plane the level at which the upper and lower teeth meet.
Sometimes the tongue or the labial mucosa the inside lining of the lips is affected by a similarly produced bit inside lower lip, termed morsicatio linguarum and morsicatio labiorum respectively. The lesions are white with thickening and shredding of mucosa commonly combined with intervening zones of erythema redness or ulceration.
The cause is chronic parafunctional activity of the masticatory system, which produces frictional, crushing and incisive damage to the mucosal surface and over time the characteristic lesions develop. Most people are aware of a cheek chewing habit, although it may be performed subconsciously. Usually the teeth are placed too far facially i. Glassblowing involves chronic suction and may produce similar irritation of the buccal mucosa.
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome and familial dysautonomia. The diagnosis is usually made on the clinical appearance alone, and biopsy is not usually indicated. The histologic appearance is one of marked hyperparakeratosis producing a ragged surface with many projections of keratin.
Typically there is superficial colonization by bacteria. There may be vacuolated cells in the upper portion of the prickle cell layer. There is a similarity between this appearance and that of hairy leukoplakialinea alba and leukoedema. The lesions are harmless, and no treatment is indicated beyond reassurance, unless the person requests it. The most common and simple treatment is construction of a specially made acrylic prosthesis that covers the biting surfaces of the teeth and protects the cheek, tongue and labial mucosa an bit inside lower lip splint.
This is either employed in bit inside lower lip short term as a habit breaking intention, or more permanently e. Psychological intervention is also reported, but does not appear to be beneficial. This phenomenon is fairly common, with one in every adults showing evidence of active lesions at any one time.
It is more common in people who are experiencing stress or psychological conditions. The prevalence in females is double the prevalence in males, and it is two or three times more prevalent in people over the age of thirty-five. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Oral and maxillofacial medicine: Retrieved 4 Bit inside lower lip Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: Oral and maxillofacial pathology K00—K06, K11—K14—, — Bednar's aphthae Cleft palate High-arched palate Palatal cysts of the newborn Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia Stomatitis nicotina Torus palatinus.
Oral mucosa — Lining of mouth. Squamous cell papilloma Keratoacanthoma Malignant: Adenosquamous carcinoma Basaloid squamous carcinoma Mucosal melanoma Spindle cell carcinoma Squamous cell carcinoma Verrucous carcinoma Oral florid papillomatosis Oral melanosis Smoker's melanosis Pemphigoid Benign mucous bit inside lower lip Pemphigus Plasmoacanthoma Stomatitis Aphthous Denture-related Herpetic Smokeless tobacco keratosis Submucous fibrosis Ulceration Riga—Fede disease Verruca vulgaris Verruciform xanthoma White sponge nevus.
Teeth pulpdentinenamel. Periodontium gingivaperiodontal ligamentcementumalveolus — Gums and tooth-supporting structures. Cementicle Cementoblastoma Gigantiform Cementoma Eruption cyst Epulis Pyogenic granuloma Congenital epulis Gingival enlargement Gingival cyst of the adult Gingival cyst of the newborn Gingivitis Desquamative Granulomatous Plasma cell Hereditary gingival fibromatosis Hypercementosis Hypocementosis Linear gingival erythema Necrotizing periodontal diseases Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis Pericoronitis Peri-implantitis Periodontal abscess Periodontal trauma Periodontitis Aggressive As a manifestation of systemic disease Chronic Perio-endo lesion Teething.
Periapical, mandibular and maxillary hard tissues — Bones of jaws. Nasopalatine duct Median mandibular Median palatal Traumatic bone Osteoma Osteomyelitis Osteonecrosis Bisphosphonate-associated Neuralgia-inducing cavitational osteonecrosis Osteoradionecrosis Osteoporotic bone marrow defect Paget's disease of bone Periapical abscess Phoenix abscess Periapical periodontitis Stafne defect Torus mandibularis.
Temporomandibular jointsmuscles of mastication and malocclusions — Jaw joints, chewing muscles and bite abnormalities. Benign lymphoepithelial lesion Ectopic salivary bit inside lower lip tissue Frey's bit inside lower lip HIV salivary gland disease Necrotizing sialometaplasia Mucocele Ranula Pneumoparotitis Salivary duct stricture Salivary gland aplasia Salivary gland atresia Salivary gland diverticulum Salivary gland fistula Salivary gland hyperplasia Salivary gland hypoplasia Salivary gland neoplasms Benign: Basal cell adenoma Canalicular adenoma Ductal papilloma Monomorphic adenoma Myoepithelioma Oncocytoma Papillary cystadenoma lymphomatosum Pleomorphic adenoma Sebaceous adenoma Malignant: Orofacial soft tissues — Soft tissues around the mouth.
Eagle syndrome Hemifacial hypertrophy Facial hemiatrophy Oral manifestations of systemic disease. Retrieved from " https: Conditions of the bit inside lower lip membranes Oral mucosal pathology Body-focused repetitive behavior Psychiatric diseases and disorders. Wikipedia articles needing page number citations from July Infobox medical condition. Views Read Edit View history. Languages Deutsch Edit links.
This bit inside lower lip was last edited on 17 Februaryat By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Palate Bednar's aphthae Cleft palate High-arched palate Palatal cysts of the newborn Inflammatory papillary hyperplasia Stomatitis nicotina Torus palatinus. Periodontium gingivaperiodontal ligamentcementumalveolus — Gums and tooth-supporting structures Cementicle Cementoblastoma Gigantiform Cementoma Eruption cyst Epulis Pyogenic granuloma Congenital epulis Gingival enlargement Gingival cyst of the adult Gingival cyst of the newborn Gingivitis Desquamative Granulomatous Plasma cell Hereditary gingival fibromatosis Hypercementosis Hypocementosis Linear gingival erythema Necrotizing periodontal diseases Acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis Pericoronitis Peri-implantitis Periodontal abscess Periodontal trauma Periodontitis Aggressive As a manifestation of systemic disease Chronic Perio-endo lesion Teething.
Periapical, mandibular and maxillary hard tissues — Bones of jaws Agnathia Alveolar osteitis Buccal exostosis Cherubism Idiopathic osteosclerosis Mandibular fracture Microgenia Micrognathia Intraosseous cysts Odontogenic: Temporomandibular jointsmuscles of mastication and malocclusions — Jaw joints, chewing muscles and bite abnormalities Bruxism Condylar resorption Mandibular dislocation Malocclusion Crossbite Open bite Overbite Overeruption Overjet Prognathia Retrognathia Scissor bite Maxillary hypoplasia Temporomandibular joint dysfunction.
Salivary glands Benign lymphoepithelial lesion Ectopic salivary gland tissue Bit inside lower lip syndrome HIV salivary gland disease Necrotizing sialometaplasia Mucocele Ranula Pneumoparotitis Salivary duct stricture Salivary gland aplasia Salivary gland atresia Salivary gland diverticulum Salivary gland fistula Salivary gland hyperplasia Salivary gland hypoplasia Salivary gland neoplasms Benign: Orofacial soft tissues — Soft tissues around the mouth Actinomycosis Angioedema Basal cell carcinoma Cutaneous sinus of dental origin Cystic hygroma Gnathophyma Ludwig's angina Macrostomia Melkersson—Rosenthal syndrome Microstomia Noma Oral Crohn's disease Orofacial granulomatosis Perioral dermatitis Pyostomatitis vegetans.
Other Eagle syndrome Hemifacial hypertrophy Facial hemiatrophy Oral manifestations of systemic disease.