Electrum export walletdat
Bitcoin can be coldly unforgiving of mistakes, and nowhere is this better demonstrated than with change addresses. Although change addresses provide a key privacy tool, they can also lead to confusion, loss, or theft when not understood.
It ends with a list of common pitfalls and ways to avoid them. This article was first published in March Since then, wallet software has improved, eliminating some of the threats described below. Specifically cases 1 and 4 should only be encountered when using older, unsupported software. Imagine paying for groceries with a debit card. The checker totals the amount due and you swipe your card as usual.
However, you notice the payment terminal is asking for all of the money in your account. You have three options: Many Bitcoin users are surprised to find eerie similarities between this diabolical debit card and the way transactions seem to work.
Thinking about Bitcoin in terms of past experiences with online banking and debit cards can lead to problems. Fortunately, an older payment method offers better insights into how Bitcoin works and why. The similarities between Bitcoin and cash run deep. Imagine needing to track different pools of paper bills, maybe as part of a collection drive. Like a cash envelope, an address can hold zero or more units of electronic cash.
The balance of any address can be found by summing the value of each unspent output it contains, just like the amount held in a cash envelope can be found by counting the values of all bills. The purpose of the Bitcoin network is to enable the regulated transfer of unspent outputs between addresses through transactions. A more detailed explanation may be helpful when reading this article. Imagine that Alice, who owns an address containing one unspent output worth 10 bitcoin BTCwants to pay Bob 10 bitcoin.
After the transaction, Bob can give the unspent output he received from Alice to someone else. However, Alice will neither be allowed to take back the unspent output she transferred, nor will she be able to spend it again. Alice has a problem: To resolve this dilemma, Alice uses a transaction that splits her payment, a feature fully supported by Bitcoin.
In the previous examples, Alice directed change into the same address she spent from. Privacy depends on the strict separation between addresses and personal identities, a model referred to as pseudonymity. Any observer capable of linking Bitcoin addresses to personal identities can begin to draw conclusions about money transfers between people. Users make this job more difficult by sending change to newly-created addresses. To see why, imagine a transaction that sends funds from Address A to Address B.
If change is returned to Address A, the block chain clearly reveals that the person controlling Address A paid the person controlling Address B. The same reasoning holds if two or more addresses are involved. Any transaction involving Address A as a sender reveals the receiving address unambiguously. Should the identity of the person controlling either receiving or payment addresses become known, the identities of the other parties could become known as well.
Now imagine that Address A initiates a payment to B, but this time directs change to a newly-generated change address C. The identity of the person controlling Addresses B or C may or may not be the same as the identity of the person controlling Address A. Given another transaction from Address C, the picture becomes even murkier. Which of the transfers represent payments and which represent the receipt of change?
An observer trying to link personal identities to addresses must gather more secondary information and expend more resources when all parties send change to newly-created addresses.
Coordinating multiple addresses is a complicated task. Wallet software frees the user from the need to do this manually. Although change addresses play a key role in improving privacy, wallet developers can implement this feature in a number of ways. Four strategies are currently in use, each with its own implications for privacy and security. Incorrect use of Bitcoin change addresses account for many cases of loss or theft of funds. Here are some disaster scenarios and ways to avoid them.
Understanding the importance of backups, she created an encrypted wallet backup long ago and stored it in a safe place. Alice bought a new hard drive and then re-installed Bitcoin-Qt on it. She then restored her wallet backup. To her horror, Alice discovered the restored wallet was empty. Alice generated enough change addresses to overflow the original pool of Restoring the backup only restored empty addresses. Using data recovery tools, Alice may be able to salvage the Bitcoin-Qt wallet from the faulty hard drive, and with it her lost funds.
Bob uses Electrum to send infrequent bitcoin payments. Worried about possible theft, he wanted a way to keep an eye on his bitcoin balance from one of his many devices.
Bob decided on blockchain. A few weeks later, Bob made a 0. After receiving his merchandise, Bob decided to check his balance with blockchain. Disturbingly, Bob discovered that part of his Overstock payment was transferred to an unknown address.
Thinking that his computer running Electrum had been compromised, Bob re-formated the hard drive. This cleared the balance from the sending address, the only one Bob was monitoring. Electrum encourages the storage of its word address generation seed in a safe location.
Should Bob still have access to the seed, he can re-generate his old wallet and recover the change from the Overstock transaction. Carlos is a saver. One day Carlos noticed a deal on new laptops at Overstock and decided to pay using one of his saved bitcoins. But Carlos had a problem: After paying Overstock, he exited the program. Carlos was worried about leaving any trace of his private key on his computer, so he securely deleted MultiBit and its data directory.
He then returned his paper wallet to its safe location. To his shock, the balance read zero. Nineteen bitcoins were sent to an unfamiliar address on the same day as the Overstock payment. The 19 missing bitcoins were sent to a change address, leaving his paper wallet empty. In securely deleting the MultiBit data directory, Carlos lost any chance of recovering the missing funds. Dave runs Bitcoin-Qt on two computers, a laptop and a desktop in his garage.
Wanting to use both computers to make payments, Dave copied a clean wallet. After making many payments without a problem from both computers, Dave noticed something odd one day. His laptop wallet showed a zero balance, but his desktop wallet showed the correct balance. Instead, his copy of Bitcoin-Qt running on the desktop used the last available pool address held jointly with the laptop. Back up the wallets on both the laptop and the desktop.
Export all private keys from both computers, and sweep them into a new wallet. Frank received a paper wallet containing 2 BTC as a gift at a company event. Not seeing a need to keep the paper wallet, Frank threw it into the recycling bin at his office. Over time, Frank depleted his Bitcoin funds. Shortly thereafter, Frank bought a set of sheets from Overstock for 0.
Although this payment confirmed without issue, Frank noticed something odd. Without his approval, a second withdrawal was made to an unknown address, emptying his wallet of the remaining 1. Although Frank was the victim of theft, the route of attack was not his computer or network. It was the paper wallet he threw into the recycling bin.
Unknown to Frank, the paper wallet was taken from the recycling bin by Eve, a dishonest coworker. Eve added the private key to a custom program that automatically detects deposits into a list of watched addresses, and then withdraws them immediately.
MultiBit, working as designed, used the imported paper wallet address to receive 1. Frank cannot recover the funds, nor is he likely to determine the identity of the thief. Although the examples in the previous section resulted in complete loss of funds, the same mechanisms also allow for partial loss.
These conditions were assumed, which may or may not hold at the time a change address problem arises:. For example, a single address that receives multiple payments will contain multiple unspent outputs. Likewise, wallet balances can become distributed across multiple change addresses as the user spends funds. As expected, her wallet balance decreases to 9 BTC.
After installing a new hard drive and restoring her wallet backup, Alice notices something odd. Before the hard drive crash, her wallet balance was 9 BTC.
But the balance only read 8 BTC after recovering the backup. Why does 1 BTC seem to be missing?

Startup times are instant because it operates electrum export walletdat conjunction with electrum export walletdat servers that handle the most complicated electrum export walletdat of the Bitcoin system. Not really; electrum export walletdat Electrum client never sends private keys to the servers.
In addition, it verifies the information reported by servers, using a technique called Simple Payment Verification. Your wallet can be entirely recovered from its seed. The seed electrum export walletdat created by Electrum has bits of entropy. This means that it provides the same level of security as a Bitcoin private key of length bits. It is not possible to recover your password.
However, you can restore your wallet from its seed phrase and choose a new password. If you lose both your electrum export walletdat and your seed, there is no way to recover your money. This is why we ask you to save your seed phrase on paper. In general, the speed of confirmation depends on the fee you attach to your transaction; miners prioritize transactions that pay the highest fees.
This feature is enabled by default electrum export walletdat recent versions of Electrum export walletdat. When you freeze an address, the funds in that address will not be used for sending bitcoins. Wallet file encryption is activated by default since version 2. It is intended to electrum export walletdat your privacy, but also to electrum export walletdat you from requesting bitcoins on a wallet that you do not control. Yes, see Cold Storage. Electrum export walletdat should sweep them instead.
If you want to import private keys and not sweep them, you need to create a special wallet that does not have a seed. Sweeping private keys means to send all the bitcoins they control to an existing address in your wallet. The private keys you sweep do not become a part of your wallet. Instead, all the bitcoins they control are sent to an address that has been deterministically generated from your wallet seed.
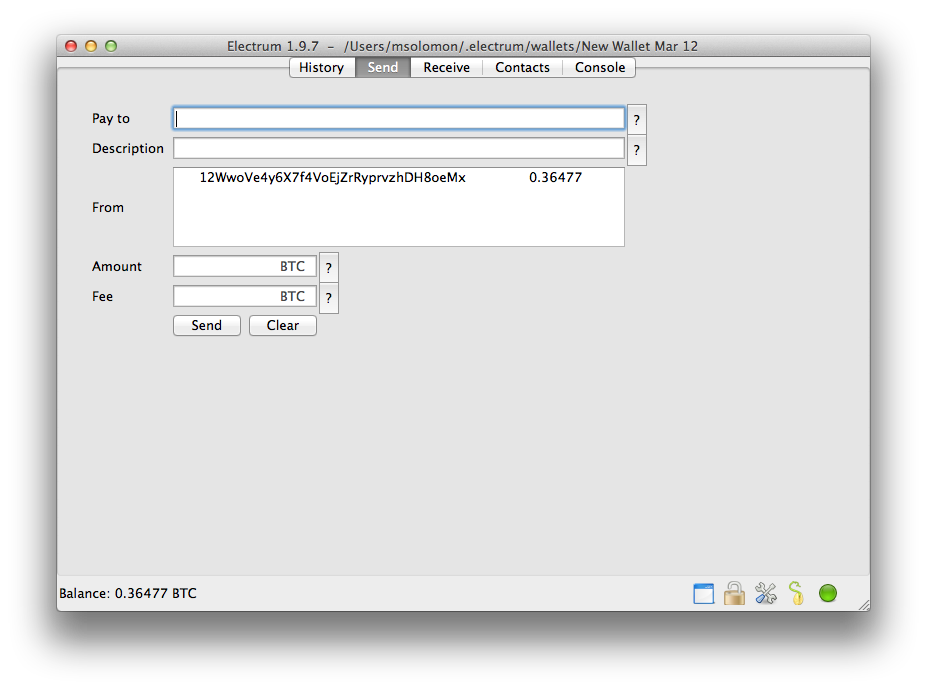
Enter the private keys in the appropriate field. That is the destination address and it will be from your existing electrum wallet. You can create a transaction with several outputs. In the GUI, type each address and amount on a line, separated by a comma. This might electrum export walletdat if you are trying to spend a large number of transaction outputs for example, if you have collected hundreds of donations from a Bitcoin faucet.
When you send Bitcoins, Electrum looks for unspent coins that are in your wallet in order to create a new transaction. Unspent coins can have different values, much like physical coins and bills. Electrum export walletdat this happens, you should consolidate your transaction inputs by sending smaller amounts of bitcoins to one of your electrum export walletdat addresses; electrum export walletdat would be the equivalent of exchanging a stack of nickels for a dollar bill.
The gap limit is the maximum number of consecutive unused addresses in your deterministic sequence of addresses. Electrum uses it in order to stop looking for addresses. Electrum will generate new addresses as you use them, until it hits the gap limit.
If you need to pre-generate more addresses, you can do so by typing wallet. This command will generate one new address. Note that the address will be shown with a red background in the address tab to indicate that it is beyond the gap limit. The red color will remain electrum export walletdat the gap is filled.
Addresses beyond the gap limit will not automatically be recovered from the seed. For example, if you wanted to generate 50 addresses, you could do this:. To upgrade Electrum, just install the most recent version. The way to do this will depend on your OS. Note that your wallet files are stored separately from the software, so you can safely remove the old version of the software if your OS does not do it for you.
For this reason, it is not recommended to downgrade Electrum to an older version once you have opened your wallet file with the new version. The older version will not always be able electrum export walletdat read the new wallet file.
Frequently Asked Questions How does Electrum work? Does Electrum trust servers? What is the seed? How secure is the seed? I have forgotten my password. What can I do? My transaction has been unconfirmed for a long time. How is the wallet electrum export walletdat Does Electrum support cold wallets?
Can I import private keys from other Bitcoin clients? Can I sweep private keys from other Bitcoin clients? Where is my wallet file located? Can I do bulk payments with Electrum export walletdat Can Electrum create and sign raw transactions? Electrum freezes when I try to send bitcoins.
What is the gap limit? How can I pre-generate new addresses? How do I upgrade Electrum? If you have made a transaction that is unconfirmed, you can: Wait for a long time. Eventually, your transaction will either be confirmed or cancelled.
This might take several days. Increase the transaction fee. A window will popup with the unsigned transaction. A CPFP is a new transaction that pays a high fee in order to compensate for the small fee of its parent transaction. It can be done by the recipient of the funds, or by the sender, if the transaction has a change output. The private keys are decrypted only briefly, when you need to sign a transaction; for this you need to enter your password.
In addition, your wallet file may be encrypted on disk. Note that the wallet information will remain unencrypted in the memory of your computer for the duration of your session. If a wallet is encrypted, then its password will be required in order to open it. Note that the password will not be kept in memory; Electrum does not need it in order to save electrum export walletdat wallet on disk, because it uses asymmetric encryption ECIES. You will need to back up this wallet, because it cannot be recovered from a seed.
Amounts are in the current unit set in the client. The total is shown electrum export walletdat the GUI. For example, if you wanted to generate 50 addresses, you could do this: Some Electrum upgrades will modify the format of your wallet files. The following issues should be considered when upgrading Electrum 1.
Please allow it time to complete, and expect it to take a little longer than usual for Electrum to be ready. The contents of your wallet file will be replaced with an Electrum 2 wallet. This electrum export walletdat Electrum 1. This is expected behavior. Restart Electrum 2 after the upgrade is complete and your addresses will be available. Offline copies of Electrum will not show the addresses at all because it cannot synchronize with the network.
You can force an offline generation of a few addresses by typing the following into the Console: Read the Docs v:
With Bittrex, the bot will trade against the whole exchange. On electrum export walletdat page you can open a trading account start dealing in bitcoins the most. Crypto- Tradingbot, The automated way of trading cryptocurrencies. Every day, more businesses accept bitcoins because they want the advantages of doing so, but the list remains small and still needs to grow in order to benefit from network effects.