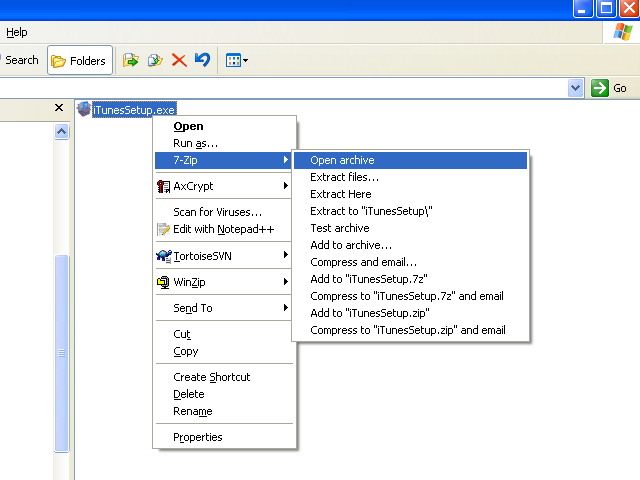
32-Bit vs. 64-Bit OSes: What's the Difference?
5 stars based on
31 reviews
The AMD K8 processor was the first to implement the architecture; this was the first significant addition to the x86 architecture designed by a company other than Intel. Intel was forced to follow suit apple application support 32 bit and 64 bit both installed by enterprise introduced a modified NetBurst family which was fully software-compatible with AMD's design and specification.
The x specification is distinct from the Intel Itanium architecture formerly IAwhich is not compatible on the native instruction set level with the x86 architecture. Originally announced in [14] while a full specification became available in August[15] the AMD64 architecture was positioned by AMD from the beginning as an evolutionary way to add bit computing capabilities to the existing x86 architecture, as opposed to Intel's approach of creating an entirely new bit architecture with IA The primary defining characteristic of AMD64 is the availability of bit general-purpose processor registers for example, rax and rbxbit integer arithmetic and logical operations, and bit virtual addresses.
The designers took the opportunity to make other improvements as well. Some of the most significant changes are described below. This would be approximately four billion times the size of apple application support 32 bit and 64 bit both installed by enterprise address space on bit machines. Most operating systems and applications will not need such a large address space for the foreseeable future, so implementing such wide virtual addresses would simply increase the complexity and cost of address translation with no real benefit.
In addition, the AMD specification requires that the most significant 16 bits of any virtual address, bits 48 through 63, must be copies of bit 47 in a manner akin to sign extension. If this requirement is not met, the processor will raise an exception. This is still 65, times larger than the virtual 4 GB address space of bit machines. This feature eases later scalability to true bit addressing. Many operating systems including, but not apple application support 32 bit and 64 bit both installed by enterprise to, the Windows NT family take the higher-addressed half of the address space named kernel space for themselves and leave the lower-addressed half user space for application code, user mode stacks, heaps, and other data regions.
Also, enforcing the "canonical form" of addresses by checking the unused address bits prevents their use by the operating system in tagged pointers as flags, privilege markers, etc. Intel has proposed a scheme with a five-level page table. If implemented, this would allow Intel 64 processors to support a bit virtual address space.
The operating system can also limit the virtual address space. Details, where applicable, are given in the " Operating system compatibility and characteristics " section. Details on this point are given in the " Operating system compatibility and characteristics " section of this article.
The traditional x87 FPU register stack is not included in the register file size extension in bit mode, compared with the XMM registers apple application support 32 bit and 64 bit both installed by enterprise by SSE2, which did get extended. The x87 register stack is not a simple register file although it does allow direct access to individual registers by low cost exchange operations.
Also note that bit code written for the and below cannot use the bit general-purpose registers GPRs. Long mode is the architecture's intended primary mode of operation; it is a combination of the processor's native bit mode and a combined bit and bit compatibility mode.
It is used by bit operating systems. Under a bit operating system, bit programs run under bit mode, and bit and bit protected mode applications that do not need to use either real mode or virtual mode in order to execute at any time run under compatibility mode.
Real-mode programs and programs that use virtual mode at any time cannot be run in long mode unless those modes are emulated in software. Since the basic instruction set is the same, there is almost no performance penalty for executing protected mode x86 code. This is unlike Intel's IAwhere differences in the underlying instruction set means that running bit code must be done either in emulation of x86 making the process slower or with a dedicated x86 coprocessor.
However, on the x platform, many x86 applications could benefit from a bit recompiledue to the additional registers in bit code and guaranteed SSE2-based FPU support, which a compiler can use for optimization. However, applications that regularly handle integers wider than 32 bits, such as cryptographic algorithms, will need a rewrite of the code handling the huge integers in order to take advantage of the bit registers. Legacy mode is the mode used by bit "protected mode" or "real mode" and bit operating systems.
In this mode, the processor acts like a bit x86 processor, and only bit and bit code can be executed. Historically, AMD has developed and produced processors with instruction sets patterned after Intel's original designs, but with x, roles were reversed: Intel's chairman at the time, Craig Barrettadmitted that this was one of their worst-kept secrets.
Intel's name for this instruction set has changed several times. In contrast, the initial Prescott chips February did not enable this feature. VIA Technologies introduced their first implementation of the x architecture in after five years of development by its CPU division, Centaur Technology. The processor supports a number of VIA-specific x86 extensions designed to boost efficiency in low-power appliances.
It is expected that the Isaiah architecture will be twice as fast in integer performance and four times as fast in floating-point performance as the previous-generation VIA Esther at an equivalent clock speed.
Although nearly identical, there are some differences between the two instruction sets in the semantics of a few seldom used machine instructions or situationswhich are mainly used for system programming. This is therefore of interest mainly to developers of compilers, operating systems and similar, which must deal with individual and special system instructions. In supercomputers tracked by TOPthe appearance of bit extensions for the x86 architecture enabled bit x86 processors by AMD and Intel light olive with circles, and red with circles on the diagram apple application support 32 bit and 64 bit both installed by enterprise in this section, respectively to replace most RISC processor architectures previously used in such systems including PA-RISCSPARCAlpha and othersas well as bit x86 green with dots and purple with dots on the diagrameven though Intel itself initially tried unsuccessfully to replace x86 with a new incompatible bit architecture in the Itanium processor.
Intel's Xeon Phi coprocessors, which implement a subset of x with some vector extensions, [49] are also used, along with x processors, in the Tianhe-2 supercomputer. The apple application support 32 bit and 64 bit both installed by enterprise operating systems and releases support the x architecture in long mode.
Preliminary infrastructure work was started in February for a x port. FreeBSD first added x support under the name "amd64" as an experimental architecture in 5. It was included as a standard distribution architecture as of 5. Work is currently being done to integrate more fully the x86 application binary interface ABIin the same manner as the Linux bit ABI compatibility currently works.
The NX bit is used to provide non-executable stack and heap with per-page granularity segment granularity being used on bit x Complete in-tree implementation of AMD64 support was achieved prior to the hardware's initial release because AMD had loaned several machines for the project's hackathon that year.
DOS itself is not aware of that, and no benefits should be expected unless running DOS in an emulation with an adequate virtualization driver backend, for example: Linux was the first operating system kernel to run the x architecture in long modestarting with the 2. This permits programs to be recompiled into long mode while retaining the use of bit programs. Several Linux distributions currently ship with xnative kernels and userlands.
Some, such as Arch Linux[59] SUSEMandrivaand Debian allow users to install a set of bit components and libraries when installing off a bit DVD, thus allowing most existing bit applications to run alongside the bit OS.
Other distributions, such as FedoraSlackware and Ubuntuare available in one version compiled for a bit architecture and another compiled for a bit architecture. Fedora and Red Hat Enterprise Linux allow concurrent installation of all userland components in both 32 and bit versions on a bit system. Mac OS X No other libraries or frameworks work with bit applications in Mac OS X The kernel, and all kernel extensions, are bit only. However, not all bit computers can run the bit kernel, and not all bit computers that can run the bit kernel will do so by default.
The bit kernel does not support bit kernel extensionsand the bit kernel does not support bit kernel extensions. In Mac OS X Solaris 10 and later releases support the x architecture. The default behavior is to boot a bit kernel, allowing both bit and existing or new bit executables to be run. A bit kernel can also be manually selected, in which case only bit executables will run. The isainfo command can be used to determine if a system is running a bit kernel.
For Solaris 11, only the bit kernel is provided. However, the bit kernel supports both and bit executables, libraries, and system calls. Windows Vistawhich also has many different editions, was released in January Windows Server R2 was sold in only x64 and Itanium editions; later versions of Windows Server only offer an x64 edition. Since AMD64 and Intel 64 are substantially similar, many software and hardware products use one vendor-neutral term to indicate their compatibility with both implementations.
The term IA refers to the Itanium processor, and should not be confused with x, as it is a completely different instruction set. Many operating systems and products, especially those that introduced x support prior to Apple application support 32 bit and 64 bit both installed by enterprise entry into the market, use the term "AMD64" or "amd64" to refer to both AMD64 and Intel Intel entered into a cross-licensing agreement with AMD, licensing to AMD their patents on existing x86 techniques, and licensing from AMD their patents on techniques used in x From Wikipedia, the apple application support 32 bit and 64 bit both installed by enterprise encyclopedia.
For the Intel bit architecture in Itanium chips, see IA Canonical address space implementations diagrams not to scale. Retrieved November 23, Intel XNU bug report". Retrieved May 27, Unlike some bit processor architectures, the POWER and x hardware does not emulate bit mode. Therefore applications that do not benefit from bit features can run with full performance on the bit version of WebSphere running on the above mentioned bit platforms.
Archived from the original on Physical address space increased to 48 bits. Archived from the original PDF on October 10, Retrieved May 30, Retrieved 19 March Retrieved January 20, Retrieved June 17, VIA's new low-power architecture". Archived from the original PDF on September 7, Retrieved July 31, General-Purpose and System Instructions".
The Old New Thing. Retrieved June 21, Archived from the original on September 10, The kernel, compiler, tool chain work.