Cryptocurrency
5 stars based on
67 reviews
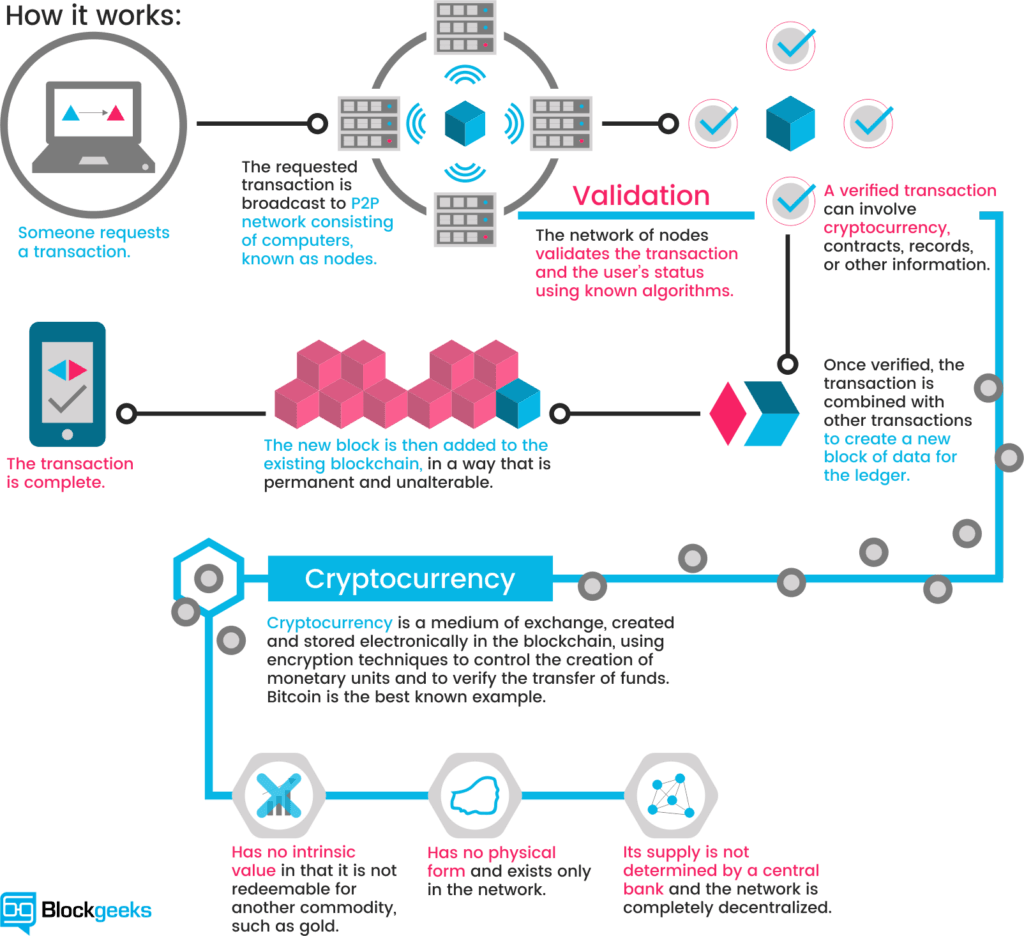
First is public key cryptography. When you send some bitcoins to someone, you bitcoin cryptography definition a message transactionattaching the new owner's public key to this amount of coins, and sign it with your private key. When this transaction is broadcast to the bitcoin network, this lets everyone know that the new owner of these coins is the owner of the new key. Your signature on the message verifies for everyone that the message is authentic. The complete history of transactions is kept by everyone, so anyone can verify who is the current owner of any particular group of coins.
This complete record of transactions is kept in the block chainwhich is a sequence of records called blocks.
All computers in the network bitcoin cryptography definition a copy of the block chain, which they keep updated by passing along new blocks to each other.
Each block contains a group of transactions that have been sent bitcoin cryptography definition the previous block. In order to preserve the integrity of the block chain, each block in the chain confirms the integrity of the previous one, all the way back to the first one, the genesis block.
Record insertion is costly because each block must meet certain requirements that make it difficult to generate a valid block. This way, no party can overwrite previous records by just forking the chain. To make generating bitcoins difficult the Hashcash cost-function is used. Hashcash is the first secure efficiently verifiable cost-function or proof-of-work function.
The beauty of hashcash is that is is non-interactive and has no secret keys that have to be managed by a central server or relying party; hashcash is as a result fully distributed and infinitely scalable. In bitcoin, integrity, block-chaining, and the hashcash cost-function all use SHA as the underlying bitcoin cryptography definition hash function.
A cryptographic hash function essentially takes input data which can be of practically any size, and transforms it, in an effectively-impossible to reverse or to predict way, into a relatively compact string in the case of SHA the hash is 32 bytes. Making the slightest change to the input data changes its hash unpredictably, so nobody can create a different block of data that gives exactly the bitcoin cryptography definition hash.
Therefore, by being given a compact hash, you can confirm that it matches only a particular input datum, and in bitcoin the input data being a bitcoin cryptography definition is significantly larger than the SHA hash. This way, Bitcoin blocks don't have to contain serial numbers, as blocks can be identified by their hash, which serves the dual purpose of identification as well as integrity verification.
An bitcoin cryptography definition string that also provides its own integrity is called a self-certifying identifier. The hashcash difficulty factor is achieved by requiring that the hash output has a number of leading zeros.
Technically, to allow more fine-grained control than Hashcash number of leading 0-bits method, Bitcoin extends the hashcash solution definition by treating the hash as a large big-endian integer, and checking that the integer is below a certain threshold. The hashcash cost-function iterates by perturbing data in the block by a nonce value, until the data in the block hashes to bitcoin cryptography definition an integer below the threshold - which takes a lot of processing power.
This low hash value for the block serves as an easily-verifiable proof of work - every node on the network can instantly verify that the block meets the required criteria. With this framework, we are able to achieve the essential functions of the Bitcoin system. We have verifiable ownership of bitcoins, and a distributed database of all transactions, which prevents double spending. We have mentioned in the previous section that adding a block to the block chain is difficult, requiring time and bitcoin cryptography definition power to bitcoin cryptography definition.
The incentive to put bitcoin cryptography definition this time and electricity is that the person who manages to produce a block gets a reward. This reward is two-fold. First, the block producer gets a bounty of some number of bitcoins, which is agreed-upon by the network. Currently this bounty is 25 bitcoins; this value will halve everyblocks. Second, any transaction fees that may be present bitcoin cryptography definition the transactions included in the block, get claimed by the block producer.
This gives rise to the activity known as "Bitcoin mining " - using processing power to try to produce a valid block, and as a result 'mine' some bitcoins. The network rules are such that the difficulty is adjusted to keep block production to approximately 1 block per 10 minutes. Thus, the more miners engage in the mining activity, the more difficult it becomes for each individual miner to produce a block.
The higher the total difficulty, the harder it is for an attacker to overwrite the tip of the block chain with bitcoin cryptography definition own blocks which enables him to double-spend his coins. See the weaknesses page for more details. Besides being important for maintaining the transaction database, mining is also the mechanism by which bitcoins get created and bitcoin cryptography definition among the people in the bitcoin economy.
The network rules are such that over the next hundred years, give or take a few decades, a total of 21 million bitcoins will be created. See Controlled Currency Supply. Rather than dropping money out of a helicopter, the bitcoins are awarded to those who contribute to the network by creating blocks in the block chain. The block chain is a common ledger shared by all Bitcoin nodes which details the owner of each bitcoin, or fraction thereof.
Unlike conventional banking systems, there is no central place where this ledger of transactions is stored. This is accomplished through the broadcasting of small pieces "blocks"each stating that it is a continuation of a previous block. It is possible for the block chain to split; that is, bitcoin cryptography definition is possible for two blocks bitcoin cryptography definition both point to the same parent block and contain some, but not all, of the same transactions.
When this happens, each computer in the network must decide for itself which branch is the "correct" one that should be accepted and extended further. The rule in this case is to accept the "longest" valid branch. Choose from the branches of blocks that you have received, the path, the total "difficulty" of which is the highest. This is the sequence of blocks that is assumed to have required the most work Bitcoin cryptography definition time to generate.
For Bitcoin, this will be the "true" order of events, and this is what it will take into account when calculating the balance to show to the user. It is still possible that, as new blocks are constantly being generated, at some later time, some other branch will become the longest branch. However, it takes significant effort to extend a branch, and nodes work to extend the branch that they have received and accepted which is normally the longest one.
So, the longer this branch becomes compared to the second-longest branch, the more effort it will take for the second-longest branch to catch up and overcome the first in length. Also, the more nodes in the network hear about the longest branch, the more unlikely it becomes for other branches to be extended the next time a block bitcoin cryptography definition generated, since the nodes will accept the longest chain.
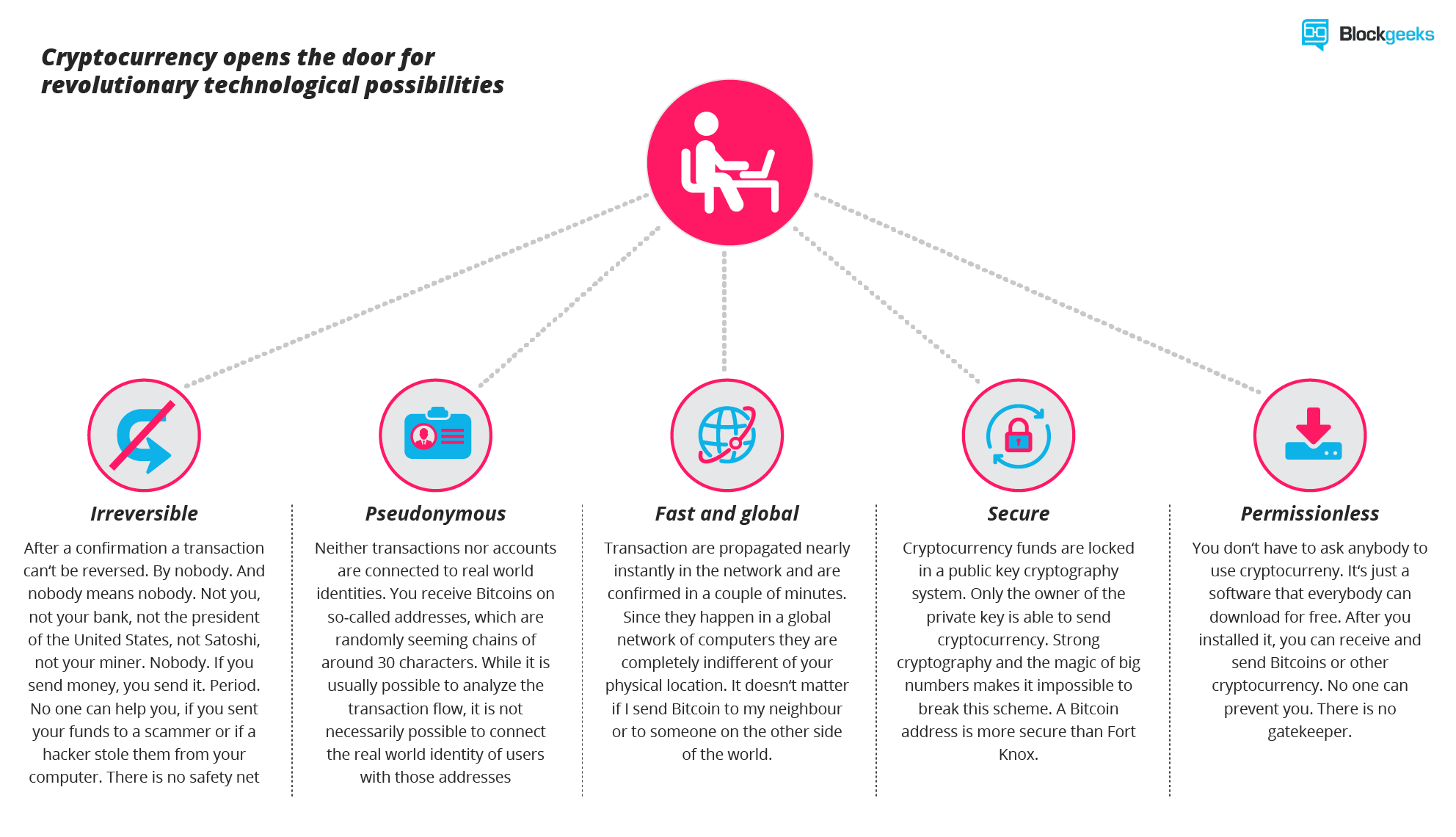
Therefore, the more time a transaction has been part of the longest block chain, the more likely it is to remain part of the chain indefinitely. This is what makes bitcoin cryptography definition non-reversible and this is what prevents people from double-spending their coins.
When the block chain after the transaction has become long enough, it becomes near-impossible for another branch to overcome it, and so people can start accepting the transaction as true. This is why 'blocks' also serve as 'confirmations' for a transaction. Even if another branch does bitcoin cryptography definition the one with the transaction, most of the blocks will have been generated by people who have no affiliation with bitcoin cryptography definition sender of the coins, as a large number of people are working to generate blocks.
Since transactions are broadcasted to all nodes in the network, these blocks are just as likely to contain the transaction as the blocks in the previously-accepted branch. Bitcoin relies on the fact that no single entity can control most of the CPU power on the network for any significant length of time, since, if they could, they would be able to extend any branch of the tree they chose, and faster than any other branch can be extended, making it the longest branch, and then permanently controlling which transactions appear in it.
This article requires cleanup to meet the Bitcoin Wiki's quality standards. This page explains the basic framework of Bitcoin's bitcoin cryptography definition. Retrieved from " https: Navigation menu Personal tools Create account Log in.
Bitcoin cryptography definition Read View source View history. Sister projects Essays Source. This page was last edited on 4 Februaryat Content is available under Creative Commons Attribution 3.
Privacy policy About Bitcoin Wiki Disclaimers.