Cracking the Ethereum White Paper
4 stars based on
51 reviews
Ethereum is an open blockchain platform that lets anyone build and use decentralized applications that run on blockchain technology.
Like Bitcoin, ethereum white paper summary one controls or owns Ethereum — it is an open-source project built by many people around the world. But unlike the Ethereum white paper summary protocol, Ethereum was designed to be adaptable and flexible.
It is easy to create new applications on the Ethereum platform, and with the Homestead release, it is now safe for anyone to use those applications. While the use of blockchains for more general uses was already discussed in the original paper, it was not until a few years later that blockchain technology emerged as a generic term. A blockchain is a distributed computing architecture where every network node executes and records the same transactions, which are grouped into blocks.
Only one block can be added at a time, and every block contains a mathematical proof that verifies that it follows in sequence from the previous block. Individual user interactions with the ledger transactions are secured by strong cryptography.
Nodes that maintain and verify the network are incentivized by mathematically enforced economic incentives coded into the protocol. But as bitcoin began attracting greater attention from developers and technologists, novel projects began to use the bitcoin network for purposes other than transfers of value tokens.
InEthereum founders Vitalik Buterin, Gavin Wood and Jeffrey Wilcke began work on a next-generation blockchain that had the ambitions to implement a general, fully trustless smart contract platform.
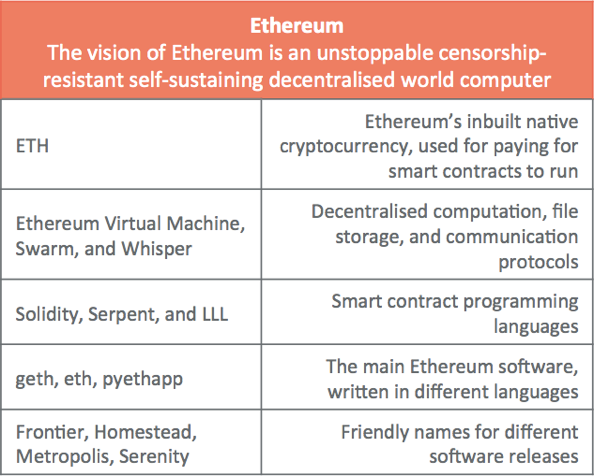
Ethereum is a programmable blockchain. Rather than ethereum white paper summary users a set of pre-defined operations e. In this way, it serves as a platform for many different types of decentralized blockchain applications, including but not limited to cryptocurrencies. Ethereum in the narrow sense refers to a suite of protocols that define a platform for decentralised applications.
Developers can create applications that run on the EVM using friendly programming languages modelled on existing languages like JavaScript and Python. Like any blockchain, Ethereum also includes a peer-to-peer network protocol. The Ethereum blockchain database is maintained and updated by many nodes connected ethereum white paper summary the network. Each and every node of the network ethereum white paper summary the EVM and executes the same instructions. This massive parallelisation of computing across the entire Ethereum network is not done to make computation more efficient.
Rather, every Ethereum node runs the EVM in order to maintain consensus across the blockchain. Decentralized consensus gives Ethereum extreme levels of fault tolerance, ensures zero downtime, and makes data stored on the blockchain forever unchangeable and censorship-resistant. The Ethereum platform itself is featureless or value-agnostic.
Similar to programming languages, it is up to entrepreneurs and developers to decide what it should be used for. Specifically, ethereum is suited for applications that automate direct interaction between peers or facilitate coordinated group action across a network. For instance, applications for coordinating peer-to-peer marketplaces, or the automation of complex financial contracts.
Ethereum white paper summary allows for individuals to exchange cash without involving any middlemen like financial institutions, banks, or governments.
Ethereum white paper summary theory, financial interactions or exchanges of any complexity could be carried out automatically and reliably using code running on Ethereum. Beyond financial applications, any environments where trust, security, and permanence are important — for instance, asset-registries, voting, governance, and the internet of things — could be massively impacted by the Ethereum platform.
Ethereum incorporates many features and technologies that will be familiar to users of Bitcoin, while also introducing many modifications and innovations of its own. The Ethereum blockchain tracks the state of every account, and all state transitions on the Ethereum blockchain are transfers of value and information between accounts. There are two types of ethereum white paper summary. For most users, the basic difference between these is that human users control EOAs - because they can control the private keys which give control over an EOA.
Contract accounts, on the other hand, are governed by their internal code. Users can create new contracts by deploying code to the blockchain. Contract accounts only perform an operation when instructed to do so by an EOA. So it is not possible for a Contract account to be performing native operations like random number generation or API calls — it can do these things only if prompted by an EOA. This is because Ethereum requires nodes to be able to agree on the outcome of computation, which requires a guarantee of strictly deterministic execution.
Like in Bitcoin, users must pay small transaction ethereum white paper summary to the network. This protects the Ethereum blockchain from frivolous or malicious computational tasks, like DDoS attacks or infinite loops.
These transaction fees are collected by the nodes that validate the network. Miners are rewarded with ether for each successful block they mine. This provides the economic incentive for people to dedicate hardware and electricity to the Ethereum network.
Any computational problem that requires orders of ethereum white paper summary more resources to solve algorithmically than it takes to verify the solution is a good candidate for proof of work. In order to discourage centralisation due to the use of specialised hardware e. If the problem requires memory as well as CPU, the ideal hardware is in fact the general computer. Introduction What is Ethereum? Learn about Ethereum How to use this guide?
The Homestead Release Web 3: How does Ethereum work? There are two types of accounts: Read the Docs v: