Ethereum code winratio is just a facet
48 comments
Dogecoin bitcointalk syscoined
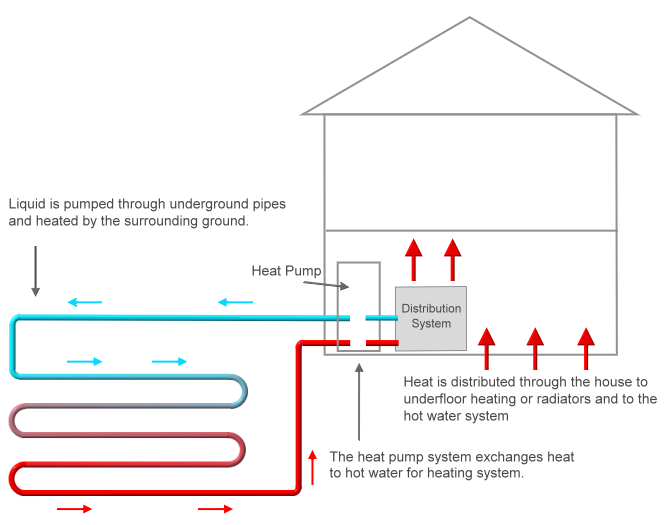
A heat pump is a device that pulls the energy out of air for the purpose of either heating or cooling a space. This process is known as space conditioning. This would seemingly violate the Second law of thermodynamics , but the key reason it doesn't is because this heat transfer is not spontaneous ; it requires an input of energy to do so. For home heating, a heat pump extracts heat from outside air, heats the warm air up even more, and transfers it indoors.
For home cooling, a heat pump reverses this process and heat is extracted from the indoor air and expelled to the outside, just like a refrigerator or air conditioner , thereby making the inside air cooler.
The heating cycle of a heat pump works by taking heat in from air outside, warming it up further, and using this warm air to heat indoor air.
It does so by the following process: The cooling cycle of a heat pump is used to cool a space by removing heat from it and expelling it to another area, usually to the outdoors for air conditioning or to the room for a refrigerator. To do this, the "evaporator" and "condenser coils" switch roles and the flow of refrigerant is reversed: The performance of a heat pump is expressed by the ratio of heat output to the work needed to be input.
Essentially, this value is how much cooling or heating is being done for a person's dollar electricity isn't free after all. This ratio is known as the coefficient of performance K , represented by the equation: The higher the value for this coefficient is, the better a heat pump is transferring heat because it requires less work to do a certain amount of heat transfer.
There is a limit however, set by the laws of entropy and the second law of thermodynamics. However they are of more practical use in many cases, since certain places on Earth do not require heating.
They function by performing essentially the same cooling cycle as heat pumps. Its Use and the Environment , 4th ed. Its Use and the Environment by R. Retrieved from " http: Energy Electrical generation Power plant Flow Fuel. Geothermal Hydropower Solar Tidal Wind. Biofuel Coal Natural gas Oil Uranium.