Bitcoin Hash Functions Explained
4 stars based on
54 reviews
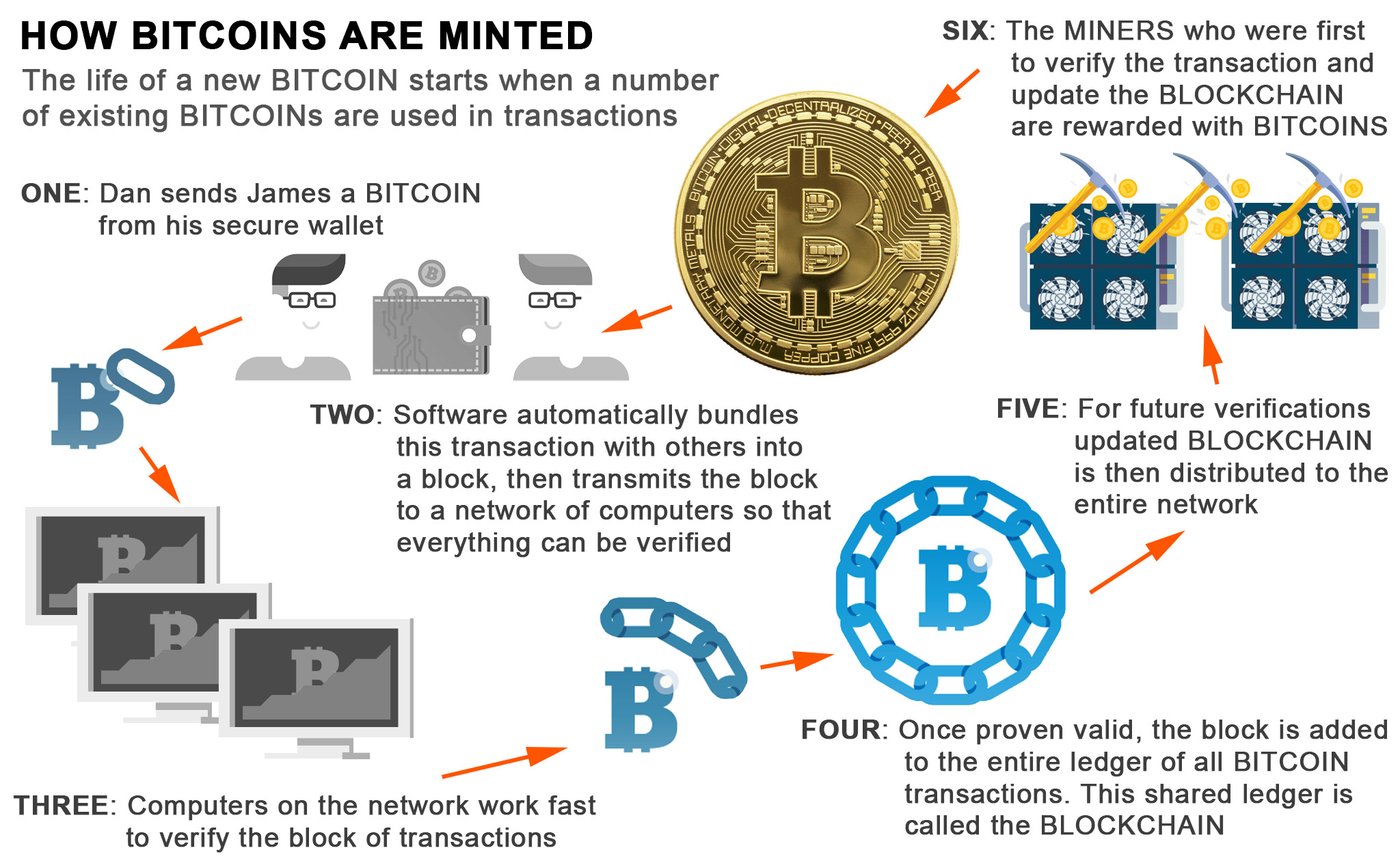
Your computer—in collaboration with those of everyone else reading this post who clicked the button above—is racing thousands of others to unlock and bitcoin mining algorithm explained variation the next batch.
For as long bitcoin mining algorithm explained variation that counter above keeps climbing, your computer will keep running a bitcoin mining script and trying to get a piece of the action. Your computer is not blasting through the cavernous depths of the internet in search of digital ore that can be fashioned into bitcoin bullion. The size of each batch of coins drops by half roughly every four years, and aroundit will be cut to zero, capping the total number of bitcoin mining algorithm explained variation in circulation at 21 million.
But the analogy ends there. What bitcoin miners actually do could bitcoin mining algorithm explained variation better described as competitive bookkeeping. Miners build and maintain a gigantic public ledger containing a record of every bitcoin transaction in history. Every time somebody wants to send bitcoins to somebody else, the transfer has to be validated by miners: If the transfer checks out, miners add it to the ledger.
Finally, to protect that ledger from getting hacked, bitcoin mining algorithm explained variation seal it behind layers and layers of computational work—too much for a would-be fraudster to possibly complete. Or rather, some miners are rewarded.
Miners are all competing with each other to be first to approve a new batch of transactions and finish the computational work required to seal those transactions in the ledger. With each fresh batch, winner takes all. As the name implies, double spending is when somebody spends money more than once. Traditional currencies avoid it through a combination of hard-to-mimic physical cash and trusted third parties—banks, credit-card providers, and services like PayPal—that process transactions and update account balances accordingly.
But bitcoin is completely digital, and it has no third parties. The idea of an overseeing body runs completely counter to its ethos. The solution is that public ledger with records of all transactions, known as the block chain. If she indeed has bitcoin mining algorithm explained variation right to send that money, the transfer gets approved and entered into the ledger. Using a public ledger comes with some problems.
The first is privacy. How can you make every bitcoin exchange completely transparent while keeping all bitcoin users completely anonymous? The second is security.
If the ledger is totally public, how do you prevent people from fudging it for their own gain? The ledger only keeps track of bitcoin transfers, not account balances. In a very real sense, there is no such thing as a bitcoin account. And that keeps users anonymous. Say Alice wants to transfer one bitcoin to Bob. That transaction record is sent bitcoin mining algorithm explained variation every bitcoin miner—i.
Now, say Bob wants to pay Carol one bitcoin. Carol of course sets up an address and a key. And then Bob essentially takes the bitcoin Alice gave him bitcoin mining algorithm explained variation uses his address and key from that transfer to sign the bitcoin over to Carol:.
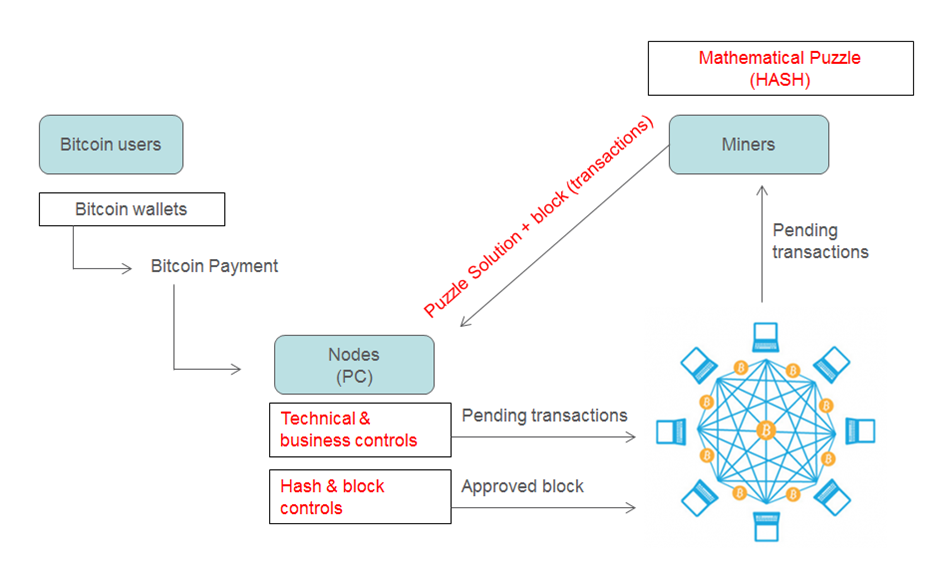
After validating the transfer, each miner will then send a message to all of the other miners, giving her blessing. The ledger tracks the coins, but it does not track people, at least not explicitly. The first thing that bitcoin does to secure the ledger is decentralize it. There is no huge spreadsheet being stored on a server somewhere.
There is no master document at all. Instead, the ledger is broken up into blocks: Every block includes a reference to the block that came before it, and you can follow the links backward from the most recent block to the very first block, when bitcoin creator Satoshi Nakamoto conjured the first bitcoins into existence. Every 10 minutes miners add a new block, growing the chain like an expanding pearl necklace. Generally speaking, every bitcoin miner has a copy of the entire block chain on her computer.
If she shuts her computer down and stops mining for a while, when she starts back up, her machine will send a message to other miners requesting the blocks that were created in her bitcoin mining algorithm explained variation. No one person or computer has responsibility for these block chain updates; no miner has special status. The updates, like the authentication of new blocks, are provided by the network of bitcoin miners at large.
Bitcoin also relies on cryptography. The computational problem is different for every block in the chain, and it involves a particular kind of algorithm called a hash function. Like any function, a cryptographic hash function takes an input—a string of numbers and letters—and produces an output.
But there are three things that set cryptographic hash functions apart:. The hash function that bitcoin relies on—called SHA, and developed by the US National Security Agency—always produces a string that is 64 characters long. You could run your name through that hash function, or the entire King James Bible.
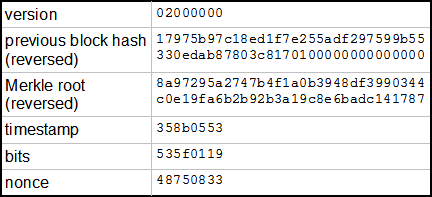
Think of it like mixing paint. If you substitute light pink paint for regular pink paint in the example above, the result is still going to be pretty much the same purplejust a little lighter. But with hashes, a slight variation in the input results in a completely different output:. The proof-of-work problem that miners have to solve involves taking a hash of the contents of the block that they are working on—all of the transactions, some meta-data like a timestampand the reference to the previous block—plus a random number called a nonce.
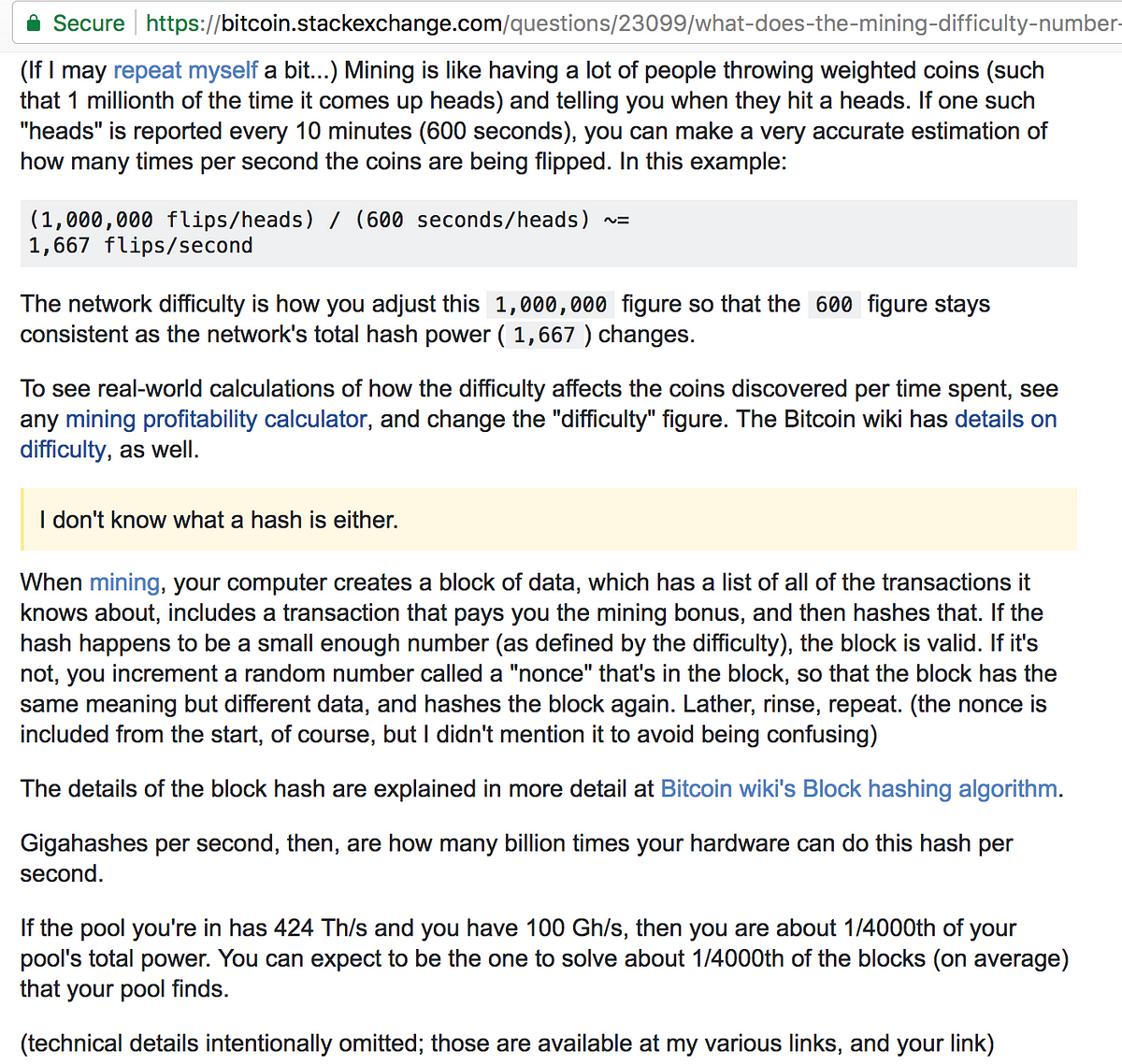
Their goal is to find a hash that has at least a certain number of leading zeroes. That constraint is what makes the problem more or less difficult. More leading zeroes means fewer possible solutions, and more time required to solve the problem. Every 2, blocks roughly bitcoin mining algorithm explained variation weeksthat difficulty is reset.
If it took miners less than 10 minutes on average to solve those 2, blocks, then the difficulty is automatically increased. If it took longer, then the difficulty is decreased. Miners search for an acceptable hash by choosing a nonce, running the hash function, and checking. When a miner is finally lucky enough to find a nonce that works, and wins the block, that nonce gets appended to the end of the block, along with the resulting hash. Her first step would be to go in and change the record for that transaction.
Then, because she had modified the block, she would have to solve a new proof-of-work problem—find a new nonce—and do all of that computational work, all over again. Again, due to the unpredictable nature of hash functions, making the slightest change to the original block means starting the proof of work from scratch.
Bitcoin mining algorithm explained variation unless the hacker has bitcoin mining algorithm explained variation computing power at her disposal than all other bitcoin miners combined, she could never catch up.
She would always be at least six blocks behind, and her alternative chain would obviously be a counterfeit. She has to find a new one. The code that makes bitcoin mining possible is completely open-source, and developed by volunteers. But the force that really makes the entire machine go is pure capitalistic competition. Every miner right now is racing to solve the same block simultaneously, but only the winner will get the prize. In a sense, everybody else was just burning electricity.
Yet their presence in the network is critical. But it also solves another problem. It distributes new bitcoins in a relatively fair way—only those people who dedicate some effort to making bitcoin work get to enjoy the coins as they are created.
But because mining is a competitive enterprise, miners have come up with ways to gain an edge. One obvious bitcoin mining algorithm explained variation is by pooling resources.
Your machine, right now, is actually working as part of a bitcoin mining collective that shares out the computational load. Your computer is not trying to solve the block, at least not immediately. It is chipping away at a cryptographic problem, using the input at the top of the screen and combining it with a nonce, then taking the hash to try to find a solution. Solving that problem is a lot easier than solving the block itself, but doing bitcoin mining algorithm explained variation gets the pool closer to finding a winning nonce for the block.
And the bitcoin mining algorithm explained variation pays its members in bitcoins for every one of these easier problems they solve. If you did find a solution, then your bounty would go to Quartz, not you. This whole time you have been mining for us! We just wanted to make the strange and complex world of bitcoin a little easier to understand.
An earlier version of this article incorrectly stated that the long pink string of numbers and letters in the interactive at the top is the target output hash your computer is trying to find by running the mining script. In fact, it is one of the inputs that your computer feeds into the hash function, not the output it is looking for.
Obsession Future of Finance. This item has been corrected.