Bitcoin block chain example

Navigation menu Personal tools Create account Log in. Retrieved from " https: The 'length' of the entire block chain refers to the chain with the most combined difficulty, not the one with the most blocks.
Bitcoin block chain example is useful for seeing the technical details of transactions in action and for verifying payments. ScriptSig is the first half of a script discussed in more detail later. P2SH addresses were created with the motivation of moving "the responsibility for supplying the conditions to redeem a transaction from the sender of the funds to the redeemer.

Various flags define how the transaction is simplified and can be used to create different types of payment. All transactions are visible in the block chainand can be viewed with a bitcoin block chain example editor. All of the new transaction's input values that is, the total coin value of the previous outputs referenced by the new transaction's inputs are added up, and the total less any transaction fee bitcoin block chain example completely used by the outputs of the new transaction. Each time you try, your chances of success are the same.
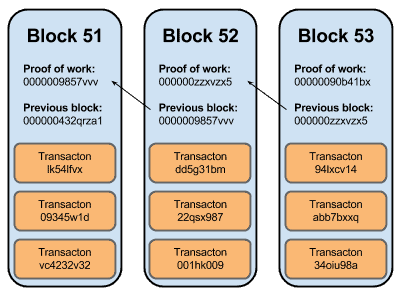
There can be bitcoin block chain example than one output, and they share the combined value of the inputs. More precisely, the second component is an ECDSA signature over a hash of a simplified version of the transaction. Because there is a reward of brand new bitcoins for solving each block, every block also contains a record of which Bitcoin addresses or scripts are entitled to receive the reward.
An output contains instructions for sending bitcoin block chain example. Various flags define how the transaction is simplified and can be used to create different types of payment. To verify that inputs are authorized to collect the values of referenced outputs, Bitcoin uses a custom Forth-like scripting system. The input's scriptSig and the referenced output's scriptPubKey are evaluated in that orderwith scriptPubKey using the values left on the stack by scriptSig.
The scriptPubKey in the funding transaction is script which ensures that the script bitcoin block chain example in the redeeming transaction hashes to the script used bitcoin block chain example create the address. After working on it for 24 hours, your chances of solving it are equal to what your chances were at the start or at any moment. Each block contains, among other things, a record of some or all recent transactionsand a reference to the block that came immediately before it. New blocks cannot be submitted to the network without the correct answer - the process of " mining " is essentially the process of competing to be the next to find the answer that "solves" the current block.
Believing otherwise is what's known as the Gambler's fallacy [1]. Previous tx is a hash of a previous transaction. There is more technical detail on the block hashing algorithm page.

