Dogecoin 280x vs tdci
31 comments
Hitbtc bitcoin exchange hack cheats
Bitcoin Core is an implementation of bitcoin. Initially, the software was published by Satoshi Nakamoto under the name "Bitcoin", and later renamed to "Bitcoin Core" to distinguish it from the network. Bitcoin Core includes a transaction verification engine and connects to the bitcoin network as a full node.
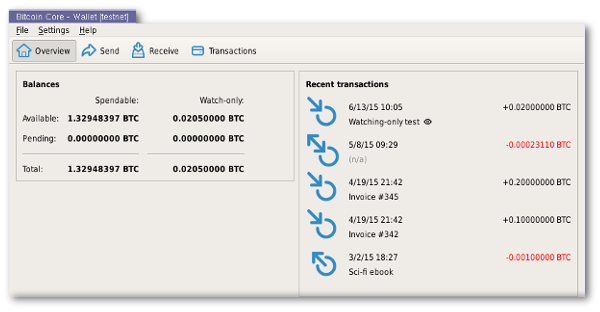
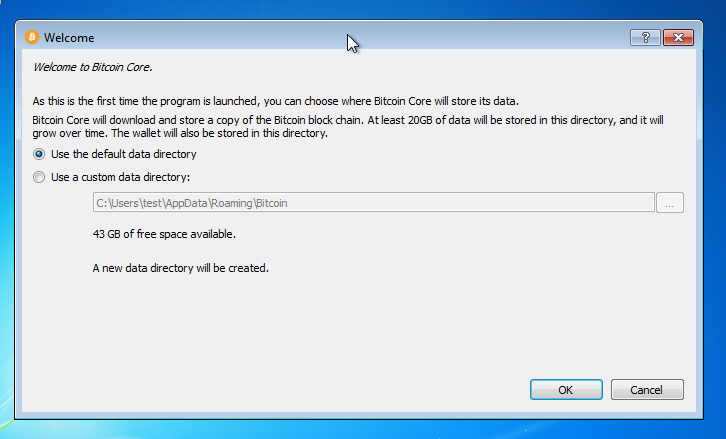
It does not facilitate the buying or selling of bitcoin. It allows users to generate QR codes to receive payment. The software validates the entire blockchain , which includes all bitcoin transactions ever. This distributed ledger which has reached more than gigabytes in size must be downloaded or synchronised before full participation of the client may occur.
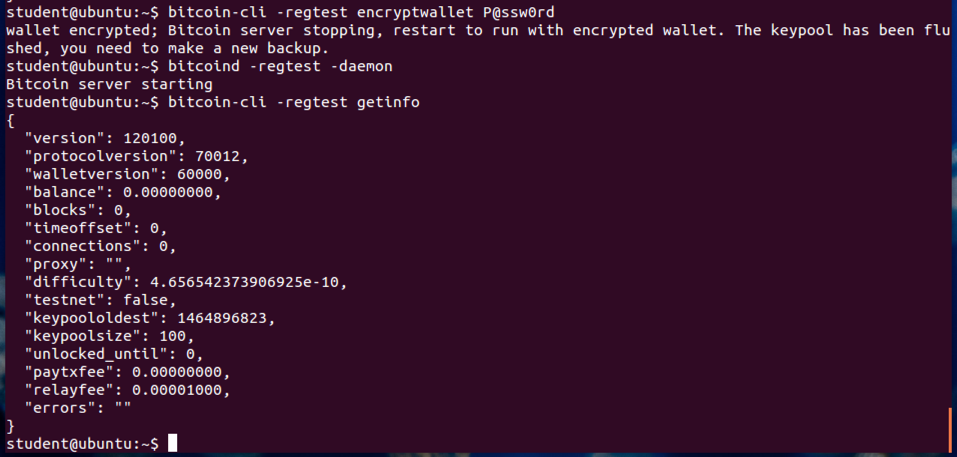
It also provides access to testnet, a global testing environment that imitates the bitcoin main network using an alternative blockchain where valueless "test bitcoins" are used. Regtest or Regression Test Mode creates a private blockchain which is used as a local testing environment. Checkpoints which have been hard coded into the client are used only to prevent Denial of Service attacks against nodes which are initially syncing the chain. For this reason the checkpoints included are only as of several years ago.
This limited the maximum network capacity to about three transactions per second. A network alert system was included by Satoshi Nakamoto as a way of informing users of important news regarding bitcoin. It had become obsolete as news on bitcoin is now widely disseminated. Bitcoin Core includes a scripting language inspired by Forth that can define transactions and specify parameters.
Two stacks are used - main and alt. The original creator of the bitcoin client has described their approach to the software's authorship as it being written first to prove to themselves that the concept of purely peer-to-peer electronic cash was valid and that a paper with solutions could be written. Andresen left the role of lead developer for bitcoin to work on the strategic development of its technology.
The code was originally stored at Sourceforge before being available on GitHub. Public mailing lists are used to vet initial expressions of ideas. This is the standard for sharing ideas and gaining community feedback on improving bitcoin and was initiated by Amir Taaki in On 16 December Bitcoin 0.
It included a Linux version for the first time and made use of multi-core processors for mining. After the release of version 0. By this time development of the software was being undertaken by a wide group of independent developers which is referred to as a community, many of whom had various ideas on how to improve bitcoin. Between and new versions of the software were released at Bitcoin. It introduced a front end that uses the Qt user interface toolkit.
Developers switched to LevelDB in release 0. The fork was resolved shortly afterwards. In this release transaction fees, also known as relay fees, were reduced from 50, satoshis to 10, satoshis.
Transaction fees were reduced again by a factor of ten as a means to encourage microtransactions. It introduced more than ten significant changes. In July , the CheckSequenceVerify soft fork activated. Launched in February , version 0.
A Bitcoin Improvement Proposal BIP is a design document, typically describing a new feature for Bitcoin with a concise technical specification of the feature and the rationale for it. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. Bitcoin Core The start screen under Fedora.
Software portal Cryptography portal Information technology portal. Retrieved 8 November Retrieved 6 November Retrieved 7 November Retrieved 14 November Retrieved 13 November Retrieved 15 November Retrieved 16 November Retrieved 19 November Bitcoin P2P e-cash paper". The Cryptography Mailing List.
The Hunt of Satoshi Nakamoto. Retrieved 23 December From Bitcoin's Inception to the Crypto-Boom". Retrieved 22 December Retrieved 25 October Archived from the original on 10 October Retrieved 10 October Retrieved 20 February History Economics Legal status. List of bitcoin companies List of bitcoin organizations List of people in blockchain technology. Free and open-source software. Alternative terms for free software Comparison of open-source and closed-source software Comparison of source code hosting facilities Free software Free software project directories Gratis versus libre Long-term support Open-source software Open-source software development Outline.
Free software movement History Open-source software movement Organizations Events. Book Category Commons Portal. Retrieved from " https: Articles containing potentially dated statements from All articles containing potentially dated statements All articles with unsourced statements Articles with unsourced statements from November All articles lacking reliable references Articles lacking reliable references from June Articles lacking reliable references from May Views Read Edit View history.
In other projects Wikimedia Commons. This page was last edited on 6 May , at By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. The start screen under Fedora. Linux , Windows , macOS. Visualization of code changes during