Private key
4 stars based on
43 reviews
Do not send bitcoins to or import any sample keys; you will lose your money. A private key in the context of Bitcoin is a secret number that allows bitcoins to be spent. Every Bitcoin wallet contains one or more private keys, which are saved in the wallet file.
The private keys are mathematically related to all Bitcoin addresses generated for the wallet. Because the private key is the "ticket" that allows someone to spend bitcoins, it is important that these are kept secure. Private keys can be kept on computer files, but in some cases are also short enough that they can be printed on paper. Some wallets allow private keys to be imported without generating any transactions while other wallets or services require that the private key be swept.
When a private key is swept, a transaction is broadcast that sends the balance controlled by the private key to a new address in the wallet. Just as with any other bitcoin private key for address is not known formats, there is risk of swept transactions to be double-spending.
In contrast, bitcoind provides a facility to import a private key without creating a sweep transaction. This is considered very dangerous, and not intended to be used even by power users or experts except in very specific cases. Bitcoins can be easily stolen at any time, from a wallet which has imported an untrusted or otherwise insecure private key - this can include private keys generated offline and never seen bitcoin private key for address is not known formats someone else [1] [2].
In Bitcoin, a private key is a bit number, which can be represented one of several ways. Here is a private key in hexadecimal - bits in hexadecimal is 32 bytes, or 64 characters in the range or A-F. Wallet software may use a BIP 32 seed to generate many private keys and corresponding public keys from a single secret value. This is called a hierarchical deterministic walletor HD wallet for short.
The seed value, or master extended keyconsists of a bit private key and a bit chain codefor bits in total. The seed value should not be confused with the private keys used directly to sign Bitcoin transactions. Users are strongly advised to use HD wallets, for safety bitcoin private key for address is not known formats An HD wallet only needs to be backed up once typically using a mnemonic phrase ; thereafter in the future, that single backup can always deterministically regenerate the same private keys.
Therefore, it can safely recover all addresses, and all funds sent to those addresses. Non-HD wallets generate a new randomly-selected private key for each new address; therefore, if the wallet file is lost or damaged, the user will irretrievably lose all funds received to addresses generated after the most recent backup.
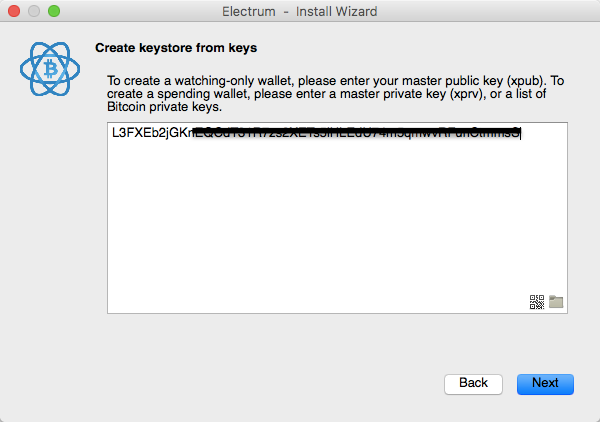
When importing or sweeping ECDSA private keys, a shorter format known as wallet import format is often used, which offers a few advantages. Wallet import format is the most common way to represent private keys in Bitcoin.
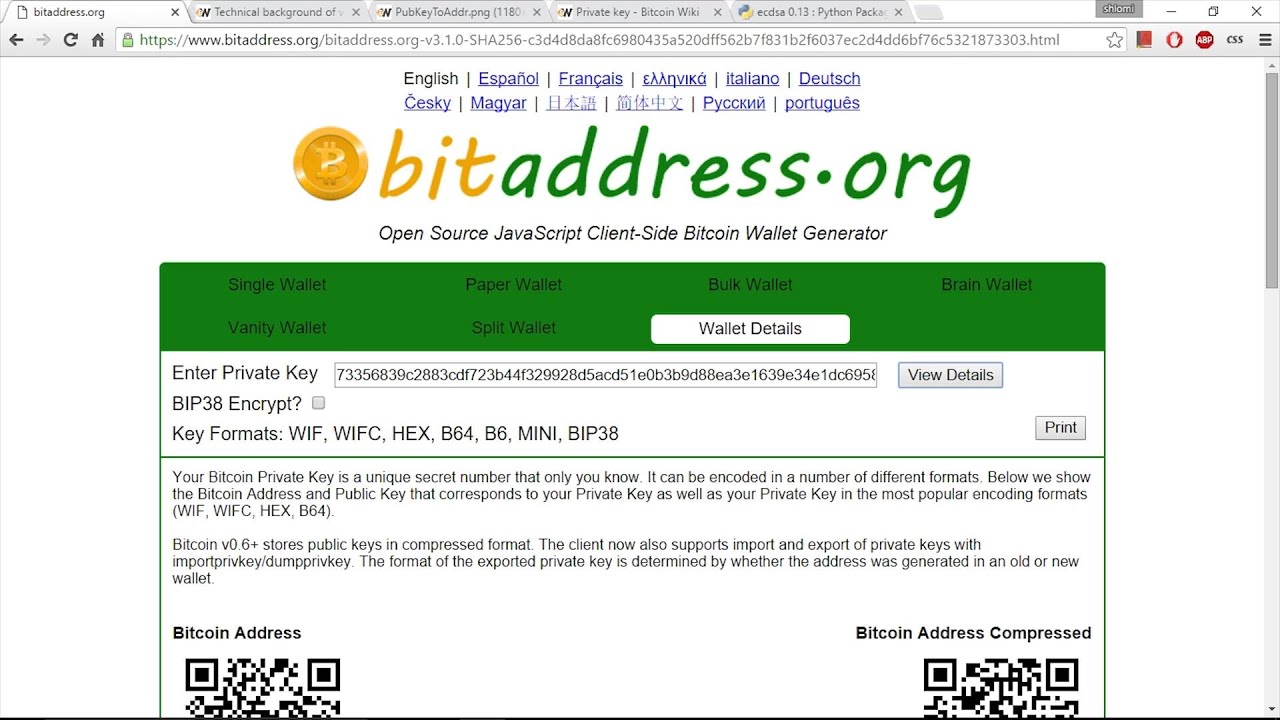
For private keys associated with uncompressed public keys, they are 51 characters and always start with the number 5 on mainnet 9 on testnet. Private keys associated with compressed public keys are 52 characters and start with a capital L or K on mainnet c on testnet. This is the same private key in mainnet wallet import format:. When a WIF private key is imported, it always corresponds to exactly one Bitcoin address. Any utility which performs the conversion can display the matching Bitcoin address.
The mathematical conversion is somewhat complex and best left to a computer, but it's notable that the WIF guarantees it will always correspond to the same address no matter which program is used to convert it. The Bitcoin address implemented using the sample above is: Some applications use the mini private key format. Not every private key or Bitcoin address has a corresponding mini private key - they have to be generated a certain way bitcoin private key for address is not known formats order to ensure a mini private key exists for an address.
The mini private key is used for applications where space is critical, such as in QR codes and in physical bitcoins. The above example has a mini key, which is:.
The private key is only needed to spend the bitcoins, not necessarily to see the value of them. If a private key controlling unspent bitcoins is compromised or stolen, the value can only be protected if it is immediately spent to a different output which is secure.
Because bitcoins can only be spent once, when they are spent using a private key, the private key becomes worthless.
It is often possible, but inadvisable and insecure, to use the address implemented by the private key again, in which case the same private key would be reused. Retrieved from " https: Navigation menu Personal tools Create account Log in.
Views Read View source View history. Sister projects Essays Source. This page was last edited on 21 Decemberat Content is available under Creative Commons Attribution 3.
Privacy policy About Bitcoin Wiki Disclaimers.
.png)