How to invest in bitcoin without getting hurt by volatility
4 stars based on
66 reviews
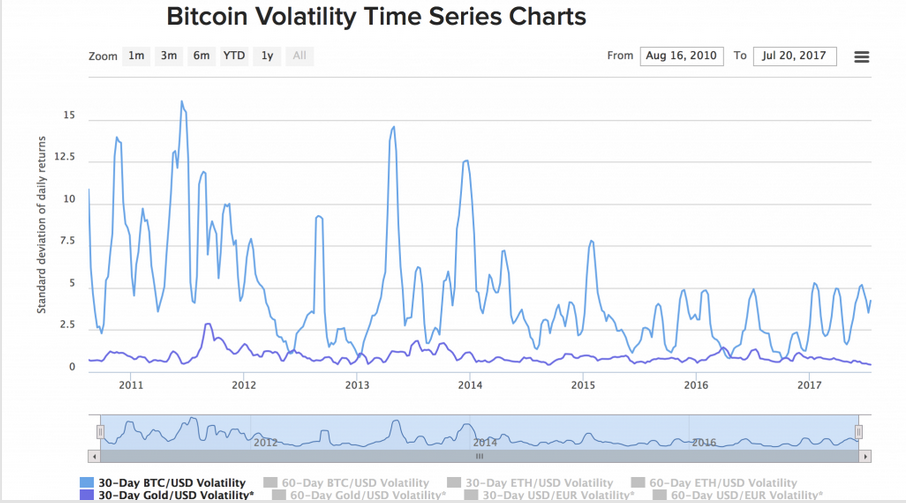
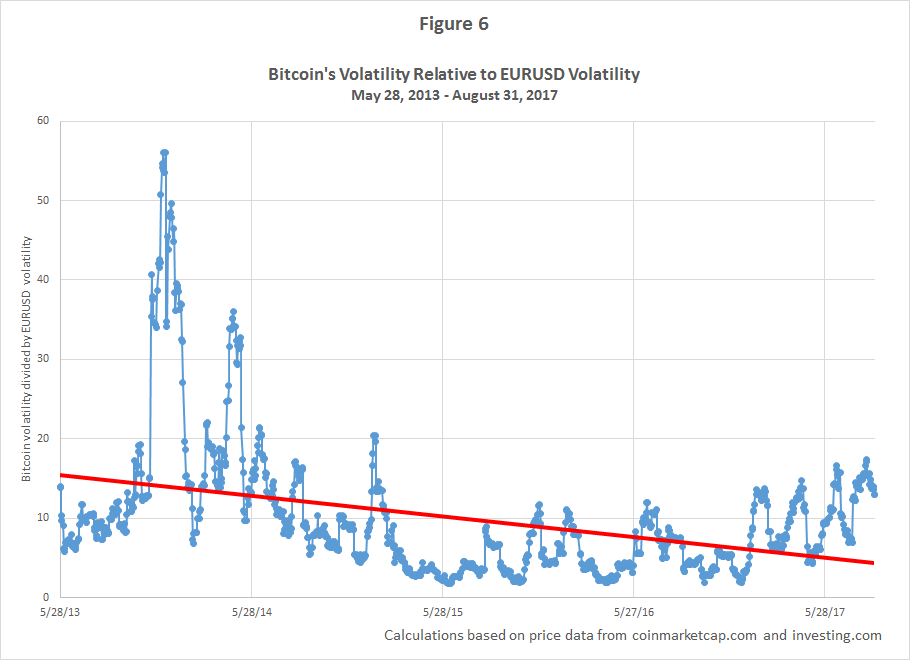
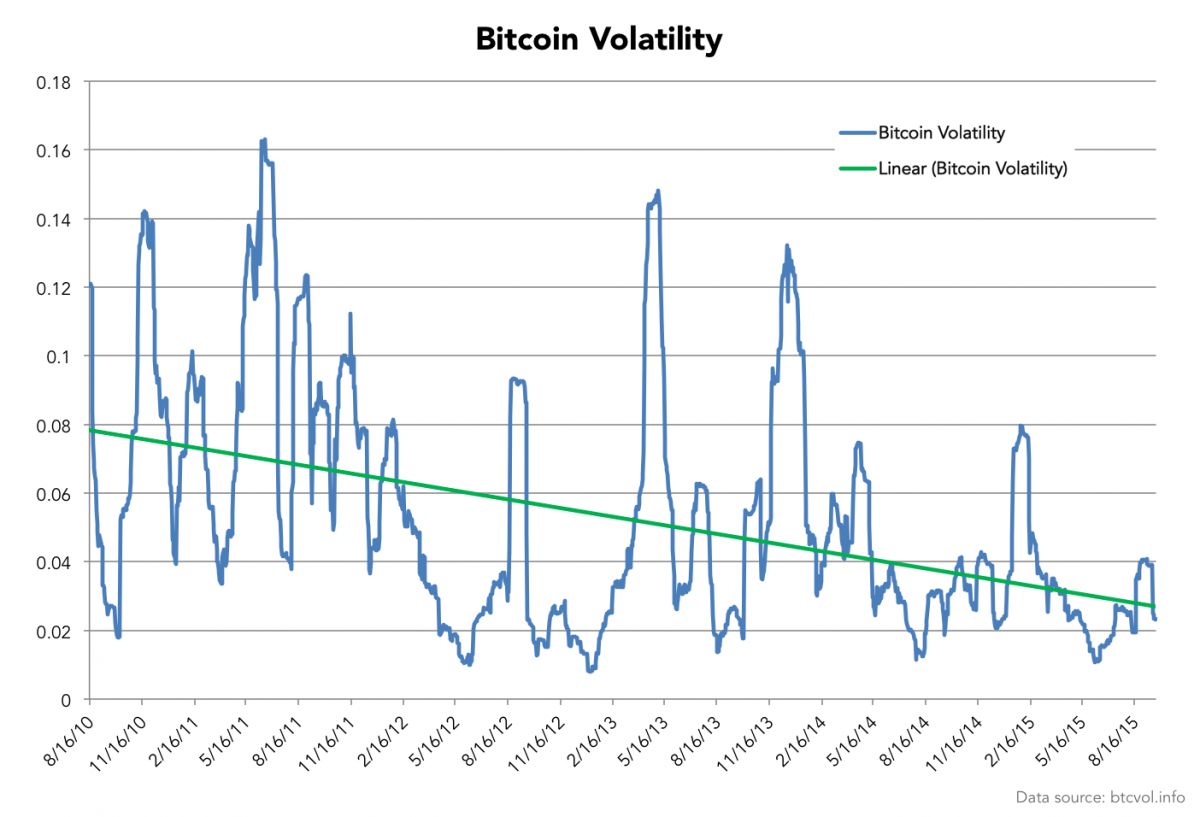
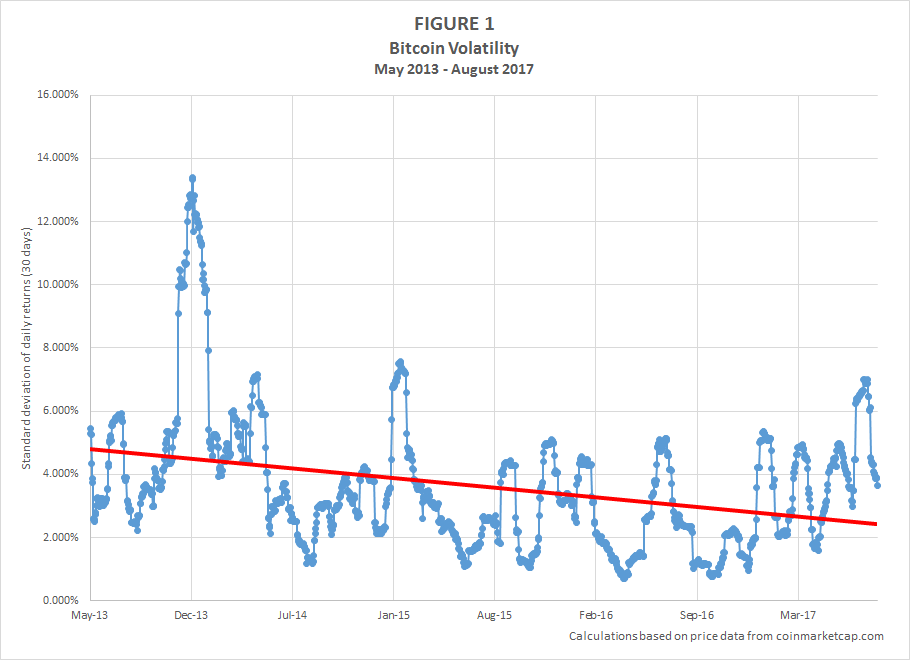
When first taking a look into the world of cryptocurrency, you may be shocked at how the price can swing, for better or bitcoin volatility 2013 spike, by a large margin. If you just take this for face value and do not look at some of the drivers that have caused the changes, you may be lost on exactly why and how the price changes.
A statistician, named Jason Schaumleffel, explains the longer term investment cycles of Bitcoin in a very digestible way:. There are currently only 16, Bitcoins in circulation, with the remaining 4, to be produced through the inflationary process of the code producing mining reward blocks every 10 minutes until around the year when the last block of 0.
This is due to the design of the system, where the code halves the reward after so many block. This halving of the reward happens about every 4 years. To complicate this some, Bitcoin can be lost or destroyed, causing the overall deflation of the currency over time, causing decreased supply. Demand is hard to judge in many cases, but you can see the trends when looking at the price charts. There are several other ways you can look into trends of demand and user base, such as number bitcoin volatility 2013 spike unique addressesnumber of transactions a day and exchange volumes.
Due to the fact that history repeats itself, this video from November has become relevant again, since it was designed to educate people on the emerging price fluctuations. Fractals are useful in modeling structures such as eroded coastlines or snowflakes in which similar patterns recur at progressively smaller scales, and in describing partly random or chaotic phenomena such as crystal growth, fluid turbulence, and galaxy formation.
As with other markets, Bitcoin has been following what seems bitcoin volatility 2013 spike be a bitcoin volatility 2013 spike pattern during it's growth cycles:. If you have found this insightful and wish to contribute with a micropayment or more, please send it to the Bitcoin address below.
This article is bitcoin volatility 2013 spike intended as financial advice and only intends to serve as a way to bitcoin volatility 2013 spike an understanding of the technology and implications of the technology. Any investment should be fully thought out and discussed with any financial advisor services you may employ before investing. The author of this article cannot be held liable for any losses incurred from your choice to invest in any of the mentioned technologies or markets in this sector.
Please invest wisely and seek proper counsel for your financial decisions. A statistician, named Jason Schaumleffel, explains the longer term investment cycles of Bitcoin in a very digestible way: Here are some of the other factors that weigh in on the price: Current Supply There are currently only 16, Bitcoins in circulation, with the remaining 4, to be produced through the inflationary process of the code producing mining reward blocks every 10 minutes until around the year when the last block of 0.
Spendable Supply - Wiki To complicate this some, Bitcoin can be lost or destroyed, causing the overall deflation of the currency over time, causing decreased supply. Demand - Who wants them and have the assets to trade Demand is hard to judge in many cases, but you can see the trends when looking at the price charts. User adoption and bitcoin volatility 2013 spike S-Curve Due to the fact that history bitcoin volatility 2013 spike itself, this video from November has become relevant again, since it bitcoin volatility 2013 spike designed to educate people on the emerging price fluctuations.
Fractals, Fibonacci and the Market What is a Fractal?