Litecoin getwork took to the season
17 comments
Arduino bitcoin price ticker
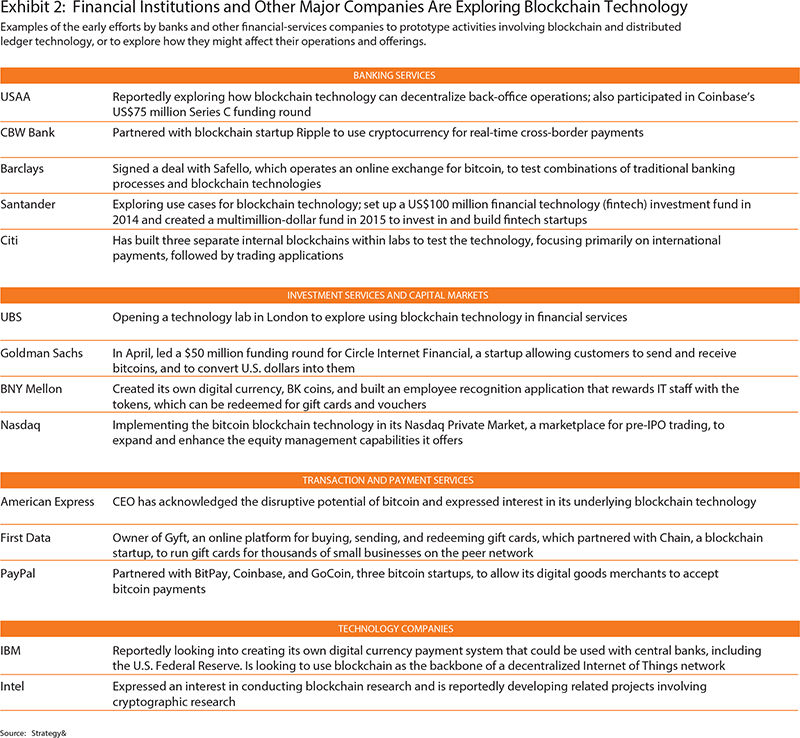
Earlier this year, IBM conducted the largest study to date on the state of adoption of blockchain. Survey responses where classified into three groups: Explorers are already involved in blockchain pilots and experiments.
They make up an average of 8 percent across all industries, with higher activity in certain industries like financial services. These survey results are not surprising for a technology as new and complex as blockchain. With such technologies, you typically have a relatively small number of early adopters.
Traditionally, intermediaries have taken on the role of trust keepers, adding costs, delays and complexity to the processing of transactions. Explorers expect blockchain to reduce transaction costs by eliminating intermediaries; increase transaction speed by reducing clearing time; and simplify and automate business processes, especially processes that deal with interactions across companies and governments. They also see blockchain as enabling the creation of platforms for business model innovation and new ways of working.
Platforms are all about scale and network effects , where the whole is much greater than the sum of their parts. Platforms require the formation of multi-sided ecosystems, including partners and developers on the supply-side, and users and customers on the demand-side. The greater trust, security and efficiencies inherent in blockchain platforms could be competitive differentiators in the formation of such multi-sided ecosystems.
Blockchain has the potential to transform our economic and social systems. Their adoption process is thus gradual, incremental and steady, unlike the hockey stick adoption we typically associate with disruptive technologies.
The impact of blockchain could well be enormous, but its full transformational impact will take considerable time. The gap between these two markets, all too frequently ignored, is in fact so significant as to warrant being called a chasm , and crossing this chasm must be the primary focus of any long term high-tech marketing plan.
A successful crossing is how high-tech fortunes are made; failure in the attempt is how they are lost. How long will it likely take? ARPANET , - the packet switching network and precursor of the Internet, - was developed by a small number of researchers in the s and s. First came universities, supercomputing centers and other research communities in the early and mid s. Then came c ommercial early adopters, who were only allowed to use the Internet toward the end of the s.
Their numbers grew rapidly over the next few years, and by the mids the Internet was being embraced by a much larger number of mainstream users, - having successfully crossed its chasm. What helped take the Internet from early adopters to mainstream users?
Three main reasons stand out for me: Its protocols, - e. The easy-to-use, graphical Mosaic web browser released in , played a major role in the popularization of the Internet. Everybody could easily appreciate the ability to easily communicate with anyone, or to access information anywhere in the world. Many other applications quickly followed across a variety of industries. In addition to developing standards and organizing technical, industry and policy activities, these various organization make available open source implementations of their software releases, thus encouraging collaborative, open innovation.
But, is blockchain ready to transition from its early adopters to a more mainstream market? There are already a number of blockchain platforms in the marketplace; more are in development. All are generally based on the original design released in by Satoshi Nakamoto , but the platforms differ, depending on the applications they are designed to support.
There seem to be two fairly distinct blockchain design points. One is primarily focused on blockchain as the underlying platform for Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies ; the second is focused on blockchains as a general purpose platform for transaction applications, - a kind of Internet 2.
The cryptocurrency-oriented platforms are mostly based on public, permissionless blockchains and proof-of-work systems. The more general purpose platforms, - e.
Some blockchain designs straddle both camps, like Ethereum , which includes support for the Ether cryptocurrency and for distributed transaction applications like smart contracts.
Does blockchain refer to the bitcoin blockchain or the technology in general? Is it a currency, commodity or technology? Is it all of these things or none of them?
Since blockchain is all about the creation, exchange and management of valuable assets, its applications are like to be considerably more complex to develop than Internet applications. It illustrates the profound differences between managing information creation versus value creation activities. The latter require deep negotiation, contractual and jurisdictional understandings, and the ongoing stewardship of application-level ecosystem.
However, this extraordinary technology may be stalled, sidetracked, captured or otherwise suboptimized depending on how all the stakeholders behave in stewarding this set of resources - i.
Is blockchain ready to cross the chasm from its early adopters into a wider marketplace? Much remains to be done. Given all the attention and activity, t his important transition should be able to take place in the not too distant future. Posted on July 31, at Very well said and very enlightening. Article helps lay out well what we "kind of know" but cannot articulate.
Blockchain is plumbing, "foundational" - and the gestation period is like the Internet Henry Perretta August 01, at This is the antidote to the euphoric 'to the moon' baseless speculation. Slow and steady, ticking the right boxes along the way instead of a flash in the pan get rich quick vehicle. Aakash Shivdasani August 01, at Athar August 04, at Irving Wladawsky-Berger A collection of observations, news and resources on the changing nature of innovation, technology, leadership, and other subjects.
Lessons from the Internet Earlier this year, IBM conducted the largest study to date on the state of adoption of blockchain. Their responses suggest that they view blockchain as a kind of trust accelerator , helping to build trust in several ways: Max Keiser and others, take note: Subscribe to this blog's feed. Subscribe to this blog via email. Blog powered by Typepad.