The truth about hashflare bitcoin cloud mining profitabilitybitcoin difficulty profit calculator
23 comments
Liquid ring vacuum pump curve
The history of Bitcoin is interesting. It has its origin in , which almost saw a complete breakdown of the US financial system. The fundamental cause of this breakdown was that financial institutions stopped trusting each other and the flow of money stopped. Luckily, the US survived the crisis and lived to tell the story. However, even today there is no clear explanation of the root cause and no guarantees that it will not happen again.
Satoshi Nakamato or whatever his real name is , a brilliant cryptographer and programmer, was fed up with the current financial system. Governments could create money whenever they wanted and cause deflation and inflation when they liked.
He thought of a currency which can not be manipulated and is transparent so that all transactions using the currency are visible and can be traced and verified by anyone. He wanted a currency not owned by a central authority but by everyone. It would be self-governed by a set of rules described and implemented in the software itself. The Bitcoin software is a program which can be installed by anyone. Clients on the Bitcoin network talk to each other on a peer to peer, production network.
Today, anyone can install the client and be part of the Bitcoin network. Bitcoin began at a time called "Genesis". At the origin, there were no coins and no transactions. Proof of Work requires all the nodes computers on the network to solve a math puzzle which is a game of chance. Any node which solves the puzzle first gets The holder of the bitcoin can then send some of their bitcoins to other people and ownership would spread around.
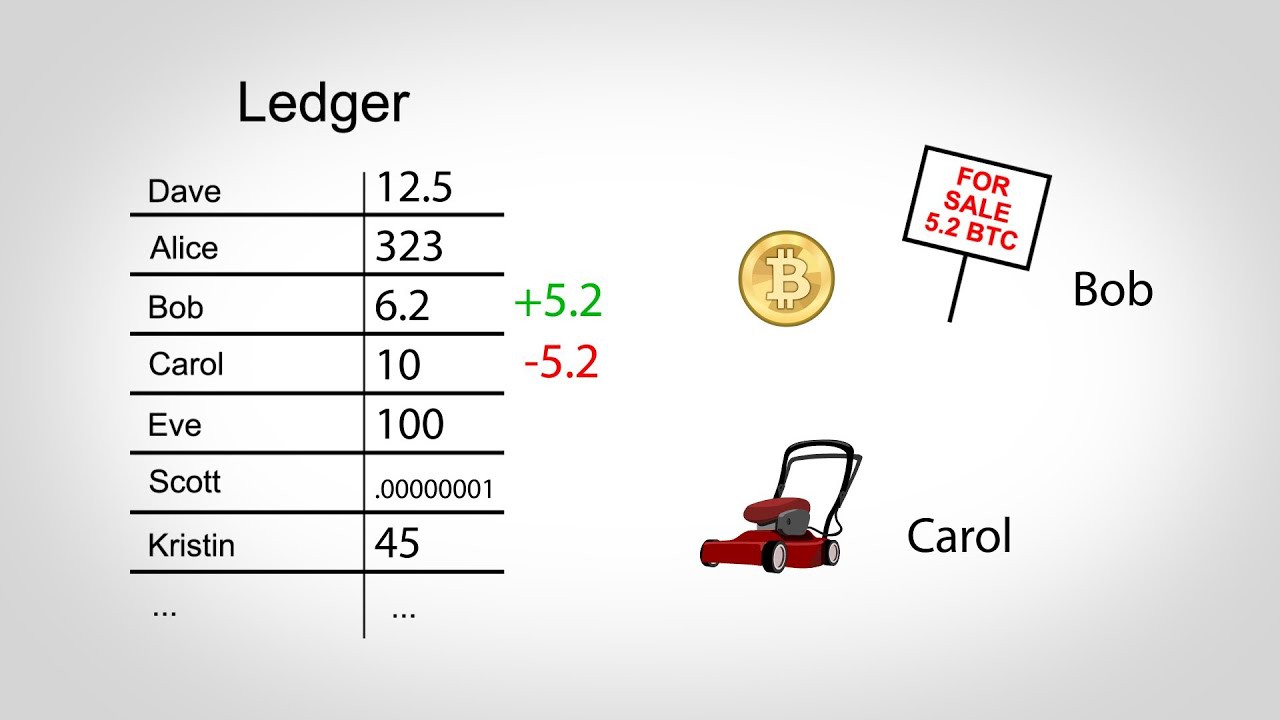
You may be asking what is the point of mining or solving the cryptographic puzzle? Mining serves 2 main functions. The ledger is considered secure because for anyone to manipulate the ledger, they have to do the work done by the miners all the way from the beginning.
So, the more the time passes and new blocks are created, the harder it gets for anyone to manipulate the ledger. How do users transact with each other? Anyone holding a bitcoin can decide to send some to an unknown person reliably and securely. All they need is the public address of the recipient party. Suppose you have no bitcoins but would like someone to send you some, all you need to do is to download a bitcoin wallet.
There are many free ones out there. Once you download a wallet, it will create a public and private key for you. Think of a public key as your email address. Think of your private key as your email password.
It is crucial to store your private key in a secure place so no one can touch it. Remember public key and private key are just random numbers but they are cryptographically produced and hold a lot of meaning in them. Now someone who wants to send you bitcoins will take your public address and will create a transaction that gives you x bitcoins and will send it to the network.
The network will then validate the transaction and some miners will include it in the newly mined block. Once your transaction is confirmed on the block, it will be announced to the world and you will know that you have bitcoin in your address.
Voila, you are now a proud owner of some bitcoin which you can spend just like cash in your pocket. Bitcoin has succeeded in bringing the first crypto-currency to the world where no single party controls it. It is all governed by software rules and no one can manipulate it single-handedly. All transactions are transparent and can be verified by anyone. The users can transact with each other anonymously without any trusted party.
Bitcoin is the future of money. First of all, whenever a new protocol or cryptocurrency comes out in the blockchain space, the founders normally write what is called a whitepaper. A whitepaper is a document which outlines the problem, solution, product, implementation, and more of a new protocol or currency.
You should always look for a whitepaper when new technology in the blockchain space is released so you can quickly get up to speed. Here is Bitcoin's Whitepaper by Satoshi Nakamoto. If you are a developer, a great resource to learn how to start developing on the Bitcoin blockchain is the Bitcoin Developer Documentation. It is very highly rated and covers all aspects of Bitcoin in detail. I love books like those because they are both surveys and yet quite deep.
I also love the entire Schaum's series of books, which I think illustrate a completely different approach to pedagogy: Here is one of those: Schaum's Outline of Probability and Statistics. I read them with an eye towards ultimately mapping them to some kind of technological implementation. Cash was an amazing invention in the history of humanity.
Let us go through some aspects of cash. Do you want to begin to understand what Bitcoin is? Well, it takes all the good aspects of cash and makes them even better. Bitcoin is digital cash. The digital cash lives in a "wallet" on your phone or computer. It is locked in your name and only you can unlock it with a secret key you have. Remember not to share your secret key with anyone.
A bitcoin is really nothing more than a balance recorded in a publically shared database. Think of a Bitcoin wallet more like a keychain. A private key look something like this: There are 3 major kinds of Bitcoin wallets we will be discussing: We will start with wallets which are the easiest to set up but offer the least security and go up to wallets which are the hardest to set up but offer the most trust.
The first kind of wallet is an online wallet. This is the easiest wallet to use but offers the least security and trust. One advantage of online wallets is that you can access them from anywhere, regardless of which device you are using. One trade-off of using an online wallet is that your private keys are stored on another server. This could lure hackers to steal your private keys, and hence your money. Gox, a popular Bitcoin exchange at the time. I personally only recommend storing bitcoins on an online wallet if you have a small quantity of them.
Some examples of online wallets are Blockchain. The second kind of wallet is a software wallet. A software wallet is a wallet installed on your computer which you have control of. You have access to your private and public key. Software wallets are available for desktop platforms as well as mobile platforms. The reference client or the standard client in which all other wallet platforms are based on is called Bitcoin Core.
This is all well and dandy except for one problem. The current size of the Bitcoin blockchain is more than GB in size. This is a real problem if you have limited storage space and limited bandwidth. Thankfully, most software clients are lightweight clients. This means they only download and communicate the pieces of information on the blockchain which matter to your Bitcoin addresses and keys. Software wallets provide more security than web wallets but greater accessibility than hardware wallets.
However, one thing to note is that they are only as secure as the computer they are stored on since the keys are on the computer. Malware on your computer can compromise your private keys.
Once you download the wallet software, it synchronizes with the network by downloading the blockchain. Once it is done, simply follow the on-screen instructions. I believe software wallets are the perfect mix of security and trust as well as usability. Examples of software wallets: Armory requires full blockchain download , Electrum and Exodus. The final type of wallet we will talk about is a hardware wallet. An hardware wallet is a dedicated piece of hardware that is built specifically to hold bitcoin's and keep them secure.
They are slightly less user-friendly than online and software wallets, but they are more secure than the other two They are great for storing large amounts of cryptocurrency and offer a lot of control. One disadvantage is that hardware wallets are in extremely high demand and are sold out often. Amazon is normally your best option to get one, however, note that it may take a while to arrive due to demand. Examples of hardware wallets: Ledger , Trezor and Keep Key. They are also a few other kinds of ways to store Bitcoin such as cold storage paper wallets and brain wallets.