A Simple Guide to What Bitcoin Forks Are and Why They Happen
4 stars based on
53 reviews
In cryptocurrenciesa fork is defined variously as. Forks are related to the fact that different parties need to use common rules to maintain the history of the blockchain. Notably, blockchain forks have been widely discussed in the context of the bitcoin scalability problem. Forks are further classified as accidental or intentional. Accidental fork happens when two or more miners find a block at nearly the same time. The fork is resolved when subsequent block s are added and one of the chains becomes longer than the alternative s.
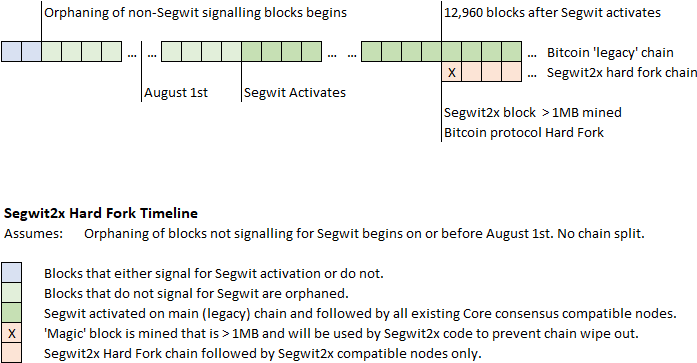
The network abandons the blocks that are not in the longest chain they are called orphaned blocks. Intentional forks that modify the rules of a blockchain can be classified as follows: A hard fork is a rule change such that the software validating according to the old rules will see the blocks produced according to the new rules as invalid. In case of a hard fork, all nodes meant to work in accordance with the new rules need to upgrade their software. If one group of nodes continues to use the old software while the other nodes use the new software, a split can occur.
For example, Ethereum has hard-forked to "make whole" the investors in The DAOwhich had been hacked by exploiting a vulnerability in its code. In the Nxt community was asked to consider a hard fork that would have led to a rollback of the blockchain records to mitigate the effects of a theft of 50 million NXT from a major cryptocurrency exchange. The hard fork proposal was rejected, and hard fork bitcoin meaning of the hard fork bitcoin meaning were recovered after negotiations and ransom payment.
Alternatively, to prevent a permanent split, a majority of nodes using the new software may return to the old rules, as was the case of bitcoin split on 12 March In contrast to a hard fork, a soft fork is a change of rules that creates blocks recognized as valid by the old software, i.
A user activated soft fork UASF is a contentious concept of enforcing a soft fork rule change without the majority support of miners. From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia. In cryptocurrenciesa fork is defined variously as "what hard fork bitcoin meaning when a blockchain diverges into two potential paths hard fork bitcoin meaning [1] "a change in protocol" [2] or a situation that "occurs when two or more blocks have the same block height" [3] [a] Forks are related to the fact that different parties need to use common rules to maintain the history of the blockchain.
User activated soft fork. If hard fork bitcoin meaning, it is also referred to as a cryptocurrency split. Retrieved 1 July Retrieved 22 March Programming the Open Blockchain 2 ed. O' Reilly media, inc.
What, Exactly, Does That Mean? Retrieved 8 March hard fork bitcoin meaning Archived from the original on Retrieved 13 November Ethereum Ethereum Classic KodakCoin. Dogecoin Gulden Litecoin PotCoin. Dash Decred Primecoin Auroracoin. Proof-of-authority Proof-of-space Proof-of-stake Proof-of-work system.
Anonymous Internet banking Bitcoin network Complementary currency Crypto-anarchism Cryptocurrency exchange Digital currency Double-spending Electronic money Initial coin offering Airdrop Virtual currency. Retrieved from " https: Pages using citations with accessdate and no URL. Views Read Edit View history. This page was last edited on 28 Marchat By using this site, you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy.