Tradings liquidations europe
36 comments
Write robot voice maker machine
Create account Login Subscribe. The cryptocurrency Bitcoin has attracted widespread interest, in large part due to wild swings in its valuation. The rise was caused by fraudulent trades taking place at the largest Bitcoin currency exchange at the time.
This finding has implications for policymakers as they weigh what, if anything, to do about regulating cryptocurrencies in light of the record high Bitcoin valuation that many fear is a bubble.
The digital currency Bitcoin was introduced in Bitcoin and the many other digital currencies are primarily online currencies. Bitcoin has experienced a meteoric rise in popularity since its introduction. While digital currencies were proposed as early as the s, Bitcoin was the first to catch on. Its success has inspired scores of competing cryptocurrencies that follow a similar design.
Bitcoin and most other cryptocurrencies do not require a central authority to validate and settle transactions. Instead, these currencies use cryptography and an internal incentive system to control transactions, manage the supply, and prevent fraud. Payments are validated by a decentralised network.
Users keep keys to their Bitcoins and make transactions with the help of wallets. Exchanges facilitate trade between Bitcoins and fiat currencies, and also allow for storing Bitcoins.
Bitcoins can be stolen through wallets or exchanges. The supply of most cryptocurrencies increases at a predetermined rate, and cannot be changed by any central authority. There are about 15 million Bitcoins currently in circulation, with the ultimate number eventually reaching 21 million. The fixed supply in the long run creates concerns about the deflationary aspect of the currency. Due to the unregulated, decentralised environment in which they operate, cryptocurrencies are under constant threat of attack.
Bitcoin only recently became a subject of research in economics. However, the topic has been of interest for longer in computer science for early work by computer scientists on incentives, see Babaioff et al. Numerous researchers have conducted studies in order to document and combat threats such as Ponzi schemes, money laundering, mining botnets, and the theft of cryptocurrency wallets Moeser et al.
Ron and Shamir attempt to identify suspicious trading activity by building a graph of Bitcoin transactions found in the public ledger. None of these papers can associate individual transactions with specific users of the currency exchanges. We leverage a unique and very detailed dataset to examine suspicious trading activity that occurred over a ten-month period in on Mt.
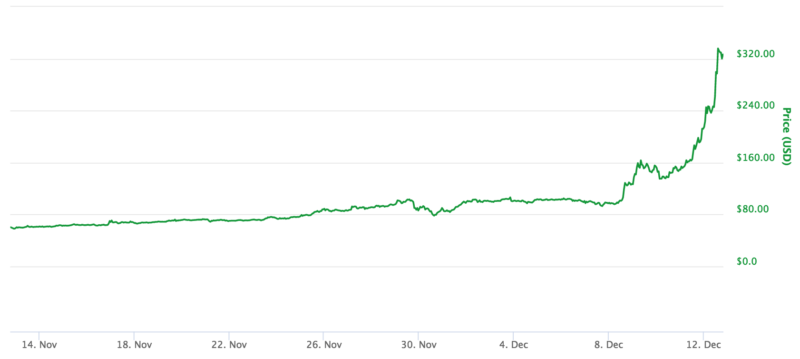
Gox, the leading Bitcoin currency exchange at the time. We then show how this trading activity affected the exchange rates at Mt. Gox and other leading currency exchanges. Figure 1 Bitcoin—US dollar exchange rate, with periods of suspicious activity shaded.
While it was the dominant currency exchange when Bitcoin first shot to prominence in early , behind the scenes, Tokyo-based Mt. Gox was in trouble. In addition to suffering from repeated denial-of-service attacks and Bitcoin thefts, two unauthorised traders were able to transact on the exchange without spending real money.
Figure 1 shows when these fraudulent traders were active, along with the Bitcoin—US dollar exchange rate. In early , Mt. Gox collapsed, and the Bitcoin price fell with it. Only recently, in early , has Bitcoin surpassed the levels of the earlier rise. However, how do we know that the rise was caused by the fraudulent trades? Fortunately for us as researchers, the unauthorised trades did not take place every day.
Table 1 shows the daily change in the Bitcoin—US dollar exchange rate for various time periods on Mt. In the two quarters before unauthorised trading commenced, the daily price increase was, on average, positive but relatively small: However, it is during the final quarter, when Willy began trading, that the difference became stark. Table 1 is very similar for the other leading exchanges as well. In our full paper, we conduct a regression analysis to examine whether other factors such as the relatively numerous and varied attacks on the Mt.
Gox exchange could explain the change in the daily Bitcoin price, both at Mt. Gox and other leading exchanges Gandal et al. The fall was nearly as precipitous: Gox exchange folded due to insolvency in early , and it has taken more than three years for Bitcoin to match the rise triggered by fraudulent transactions. Why should we care about the Bitcoin manipulation that took place in ?
Nonetheless, recent trends indicate that Bitcoin is becoming an important asset in the financial system. Trading in cryptocurrency assets has exploded recently. The market cap of other cryptocurrencies surged by even more. The markets for these other cryptocurrencies are very thin and subject to manipulation. As mainstream finance invests in cryptocurrency assets and as countries take steps toward legalising Bitcoin as a payment system as Japan did in April , it is important to understand how susceptible cryptocurrency markets are to manipulation.
We encourage the nascent cryptocurrency industry to work with regulators and researchers to share anonymised transaction data so that more confidence can be placed in the veracity of exchange rates.
He was not active on the same days as Willy, who was only active in period 4. Exchange rates Financial markets. Bitcoin , cryptocurrencies , digital currencies , price manipulation. Central banking and Bitcoin: Not yet a threat. Figure 1 Bitcoin—US dollar exchange rate, with periods of suspicious activity shaded While it was the dominant currency exchange when Bitcoin first shot to prominence in early , behind the scenes, Tokyo-based Mt.
Endnotes [1] The Bitcoin ecosystem includes the core network for propagating transactions, the blockchain, and many intermediaries such as currency exchanges, mining pools, and payment processors that facilitate trade. Research Assistant, University of Tulsa. Globalisation, government popularity, and the Great Skill Divide. The EMU after the euro crisis: Insights from a new eBook.
Spring Meeting of Young Economists Economic Forecasting with Large Datasets. Homeownership of immigrants in France: Evidence from Real Estate. Giglio, Maggiori, Stroebel, Weber. The Permanent Effects of Fiscal Consolidations. Demographics and the Secular Stagnation Hypothesis in Europe. Independent report on the Greek official debt. Step 1 — Agreeing a Crisis narrative.
A world without the WTO: The economics of insurance and its borders with general finance. Banking has taken a wrong turn.